HicAggR - In depth tutorial
Nicolas Chanard, David Depierre, Robel A. Tesfaye, Stéphane Schaak & Olivier Cuvier
2024-07-07
Source:vignettes/InDepth.Rmd
InDepth.RmdIntroduction
HicAggR package provides a set of tools for the analysis of genomic 3D conformation data (HiC). It is designed around Aggregation Peak Analysis (APA), with the intent to provide easy-to-use sets of functions that would allow users to integrate 1D-genomics data with 3D-genomics data. This package does not perform TAD calling, loop calling, or compartment analysis. There are other packages available for these analyses (eg: TopDom (from CRAN), HiTC (bioconductor), HiCDOC (bioconductor)…). The package offers however tools to perform downstream analyses on called loops,or make use of called TADs to explore interactions within loops or explore intra/inter-TAD interactions. To this end, pixels of interest surrounding called loops or genomic features are extracted from whole HiC matrices (as submatrices), abiding to TAD and/or compartmental constraints in order to give user an insight into the interaction patterns of features of interest or called loops.
Typical workflow:
The straight-forward workflow with this package would be:
- to import genomic coordinates of features of interest (such as,
enhancers, CTCF binding sites, genes) as
GRanges - apply distance constraints or 3D structural constraints (like TADs) to form all potential couples between features of interest under the applied contraints. (Enhancer-promoter, CTCF-CTCF etc.)
- import 3D-genomics data (.hic, bedpe, h5, cool/mcool formats).
- perform matrix balancing and distance normalization if necessary.
- extract submatrices of the pre-formed potential couples from the 3D-genomics Data.
- perform corrections per-submatrix
- orientation correction: i.e. set one feature of interest per axe which is to capture a uniform pattern for interactions that are towards upstream or downstream.
- ranking pixels per submatrix to highligt the most significant interaction signals per submatrix.
- summarize visually the genome-wide interactions between features of interest graphically through APA
- and/or get individual values of selected zones from each submatrix for comparison between conditions
We also propose (since version 0.99.3) a function to find couples
that demonstrate a non-random (or non-background) like interaction
signals. The function performs z.test to compare target couples to
less-plausible or background couples to identify target couples with
significantly higher interaction values than the background signal
(compareToBackground).
Quickstart and tutorials:
Please visit dedicated github pages and the github repository.
Aim:
The principal objective is to simplify the extraction of interaction
signals from HiC data, by making submatrices easy to access and treat if
necessary. As such the contact matrices are imported as a list of
ContactMatrix objects per combination of chromosomes(eg:
“chr1_chr1” or “chr1_chr2”). This allows the user to access the data
easily for dowstream analyses.
Requirements
Installation
The bioconductor release version:
if (!requireNamespace("BiocManager", quietly = TRUE))
install.packages("BiocManager")
BiocManager::install("HicAggR")The developmental version:
remotes::install_github("CuvierLab/HicAggR")Test dataset
Description
Data were obtained from Drosophila melanogaster S2 cells. 1.
HiC test dataset Directly downloaded from the 4DN platform. * Control
Condition
* Heat Shock Condition
2. Genomic coordinates:
* ChIPseq peaks of Beaf-32 protein in wild type cells (GSM1278639).
* Reference annotation data for TSS from the UCSC database.
* Topologically associating domains (TAD) annotations were defined as
described (F.
Ramirez, 2018).
1. Genomic 3D structure
For a test, please download HiC data in .hic format (Juicer) and .mcool format (HiCExplorer). Examples for each format are provided below.
Temp directory preparation
withr::local_options(list(timeout = 3600))
# temp.dir <- file.path(tempdir(), "HIC_DATA")
cache.dir <- paste0(tools::R_user_dir("", which="cache"),".HicAggR_HIC_DATA")
bfc <- BiocFileCache::BiocFileCache(cache.dir,ask = FALSE)
# dir.create(temp.dir)Control condition (.hic File)
if(length(BiocFileCache::bfcinfo(bfc)$rname)==0 ||
!"Control_HIC.hic"%in%BiocFileCache::bfcinfo(bfc)$rname){
Hic.url <- paste0("https://4dn-open-data-public.s3.amazonaws.com/",
"fourfront-webprod/wfoutput/7386f953-8da9-47b0-acb2-931cba810544/",
"4DNFIOTPSS3L.hic")
if(.Platform$OS.type == "windows"){
HicOutput.pth <- BiocFileCache::bfcadd(
x = bfc,rname = "Control_HIC.hic",
fpath = Hic.url,
download = TRUE,
config = list(method="auto",mode="wb"))
}else{
HicOutput.pth <- BiocFileCache::bfcadd(
x = bfc, rname = "Control_HIC.hic",
fpath = Hic.url,
download = TRUE,
config = list(method="auto"))
}
}else{
HicOutput.pth <- BiocFileCache::bfcpath(bfc)[
which(BiocFileCache::bfcinfo(bfc)$rname=="Control_HIC.hic")]
}Heat shock condition (.mcool File)
if(length(BiocFileCache::bfcinfo(bfc)$rname)==0 ||
!"HeatShock_HIC.mcool"%in%BiocFileCache::bfcinfo(bfc)$rname){
Mcool.url <- paste0("https://4dn-open-data-public.s3.amazonaws.com/",
"fourfront-webprod/wfoutput/4f1479a2-4226-4163-ba99-837f2c8f4ac0/",
"4DNFI8DRD739.mcool")
if(.Platform$OS.type == "windows"){
McoolOutput.pth <- BiocFileCache::bfcadd(
x = bfc, rname = "HeatShock_HIC.mcool",
fpath = Mcool.url,
download = TRUE,
config = list(method="auto",mode="wb"))
}else{
McoolOutput.pth <- BiocFileCache::bfcadd(
x = bfc, rname = "HeatShock_HIC.mcool",
fpath = Mcool.url,
download = TRUE,
config = list(method="auto"))
}
}else{
McoolOutput.pth <- as.character(BiocFileCache::bfcpath(bfc)[
which(BiocFileCache::bfcinfo(bfc)$rname == "HeatShock_HIC.mcool")])
}2 Genomic location and annotation data
These kind of data can be imported in R with rtracklayer package.
ChIPseq peaks of Beaf-32 protein
data("Beaf32_Peaks.gnr")View
| seq | start | end | strand | name | score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 35594 | 35725 | * | Beaf32_2 | 76 |
| 2L | 47296 | 47470 | * | Beaf32_3 | 44 |
| 2L | 65770 | 65971 | * | Beaf32_5 | 520 |
TSS annontation
data("TSS_Peaks.gnr")View
| seq | start | end | strand | name | class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 71757 | 71757 | + | FBgn0031213 | active |
| 2L | 76348 | 76348 | + | FBgn0031214 | inactive |
| 2L | 106903 | 106903 | + | FBgn0005278 | active |
TADs annotation
data("TADs_Domains.gnr")View
| seq | start | end | strand | name | score | class |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 73104 | 94543 | * | Tad_1 | 3 | active |
| 2L | 94544 | 102930 | * | Tad_2 | 8 | active |
| 2L | 102931 | 121473 | * | Tad_3 | 8 | active |
Additional genome informations
Required genomic informations used by the functions during the entire pipeline are a data.frame containing chromosomes names and sized and the binSize, corresponding to the HiC matrices at the same resolution.
seqlengths.num <- c('2L'=23513712, '2R'=25286936)
chromSizes <- data.frame(
seqnames = names(seqlengths.num ),
seqlengths = seqlengths.num
)
binSize <- 5000Import HiC
The package supports the import and normalization of HiC data.
NOTE: Since version 0.99.2, the package supports import of balanced HiC matrices in .hic, .cool/.mcool formats. It also supports the import of ‘o/e’ matrices in .hic format.
Import
HicAggR can import HiC data stored in the main formats: .hic, .cool, .mcool, .h5 (since version 0.99.2). The pacakage imports by default the raw counts. Therefore, it is necessary to perform the balancing and observed/expected correction steps.
Balancing
The balancing is done such that every bin of the matrix has approximately the same number of contacts within the contactMatrix.
HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst <- BalanceHiC(HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst)
HiC_HS.cmx_lst <- BalanceHiC(HiC_HS.cmx_lst)Tips
- In the interactionType parameter it is required to define “cis” or “trans”. Then the function will return only ContactMatrices in the corresponding category (“cis” or “trans”). All other categories will be removed from the result.
- In the interactionType parameter if you type c(“cis”,“trans”) the function will normalize separetly “cis” or “trans”. If you type “all” the function will normalize “cis” and “trans” matrices together.
Observed/Expected Correction
To correct effects due to genomic distance the matrix is corrected by the expected values for each genomic distance. The expected values are by default calculated as the average values of contacts per chromosome and per distance.
NOTE: Since version 0.99.3, 2 more options to calculate expected values have been implemented. We designated the methods as the “lieberman” and the “mean_total”. These methods were implemented based on the options proposed by HiCExplorer’s hicTransform program. The “lieberman” method computes per distance (d) expected values by dividing the sum of all contacts by the difference of chromosome length and distance(d).
The “mean_total” is simply the average of all contact values including 0 values, which are ignored in the default method (“mean_non_zero”)
HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst <- OverExpectedHiC(HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst)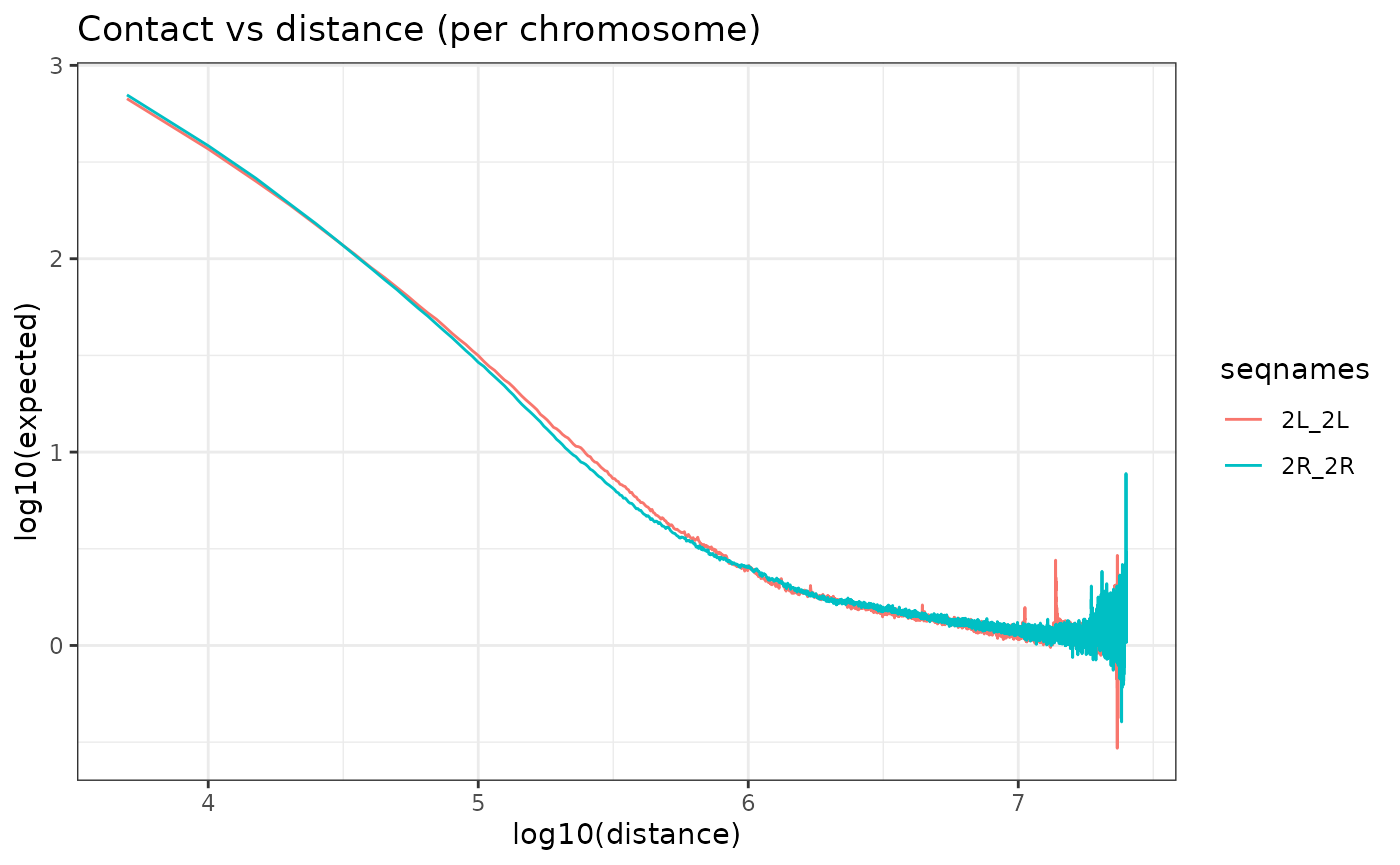
HiC_HS.cmx_lst <- OverExpectedHiC(HiC_HS.cmx_lst)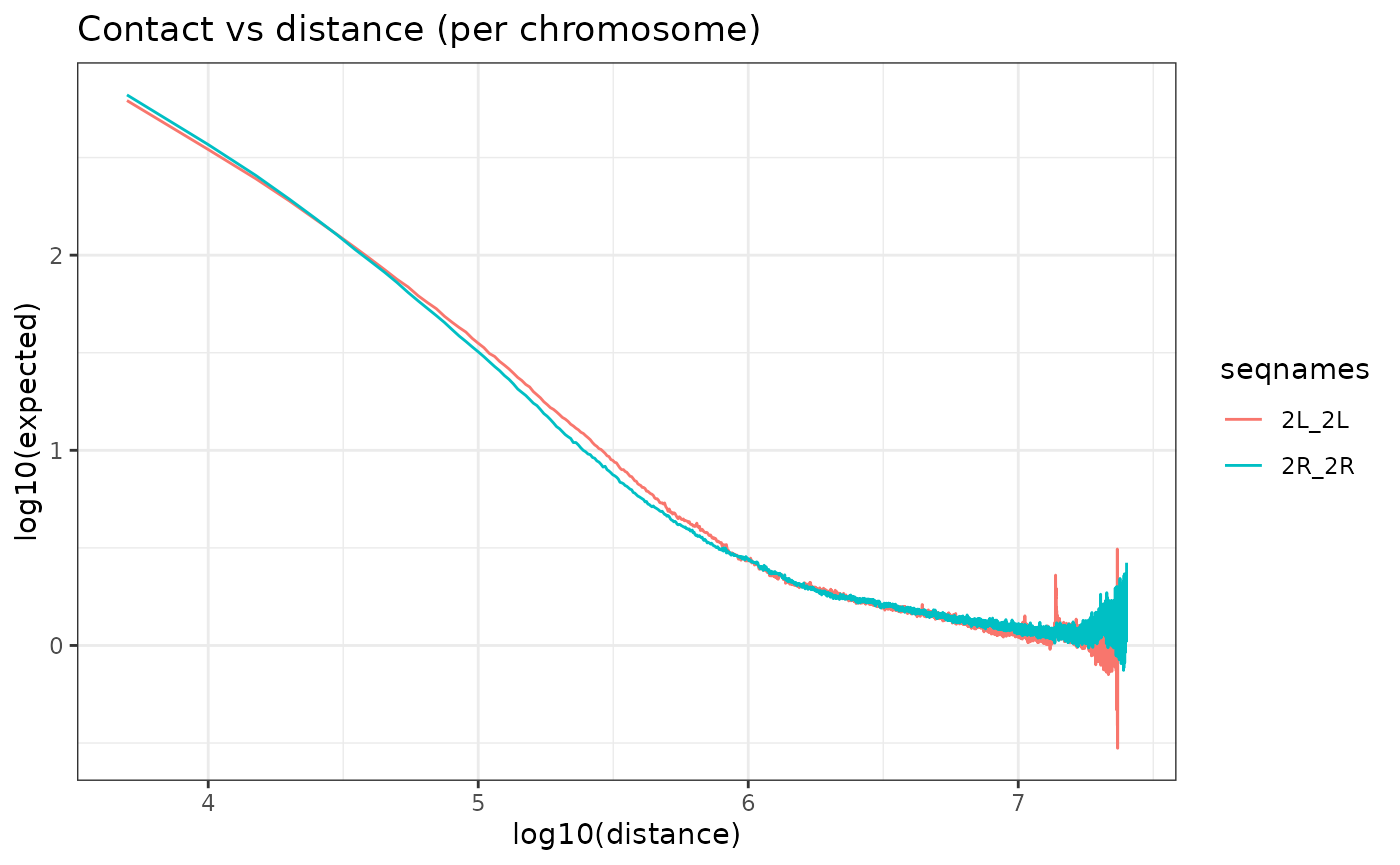
HiC data format: ContactMatrix list structure
Each element of the list corresponds to a ContactMatrix object (dgCMatrix object, sparse matrix format) storing contact frequencies for one chromosome (cis-interactions, ex: “2L_2L”) or between two chromosomes (trans-interactions, ex: “2L_2R”). HiC data format is based on InteractionSet and Matrix packages.
str(HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst,max.level = 4)
#> List of 3
#> $ 2L_2L:Formal class 'ContactMatrix' [package "InteractionSet"] with 5 slots
#> .. ..@ matrix :Formal class 'dgCMatrix' [package "Matrix"] with 6 slots
#> .. ..@ anchor1 : int [1:4703] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
#> .. ..@ anchor2 : int [1:4703] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
#> .. ..@ regions :Formal class 'GRanges' [package "GenomicRanges"] with 7 slots
#> .. ..@ metadata:List of 10
#> .. .. ..$ name : chr "2L_2L"
#> .. .. ..$ type : chr "cis"
#> .. .. ..$ kind : chr "U"
#> .. .. ..$ symmetric : logi TRUE
#> .. .. ..$ resolution : num 5000
#> .. .. ..$ expected : num [1:2410023] 719 673 719 370 673 ...
#> .. .. ..$ removedCounts:Formal class 'dgCMatrix' [package "Matrix"] with 6 slots
#> .. .. ..$ observed : num [1:2410023] 1329 1721 1852 1076 2191 ...
#> .. .. ..$ normalizer : num [1:2410023] 1.399 1.115 0.888 1.139 0.908 ...
#> .. .. ..$ mtx : chr "norm"
#> $ 2L_2R:Formal class 'ContactMatrix' [package "InteractionSet"] with 5 slots
#> .. ..@ matrix :Formal class 'dgCMatrix' [package "Matrix"] with 6 slots
#> .. ..@ anchor1 : int [1:4703] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
#> .. ..@ anchor2 : int [1:5058] 4704 4705 4706 4707 4708 4709 4710 4711 4712 4713 ...
#> .. ..@ regions :Formal class 'GRanges' [package "GenomicRanges"] with 7 slots
#> .. ..@ metadata:List of 9
#> .. .. ..$ name : chr "2L_2R"
#> .. .. ..$ type : chr "trans"
#> .. .. ..$ kind : chr NA
#> .. .. ..$ symmetric : logi FALSE
#> .. .. ..$ resolution : num 5000
#> .. .. ..$ removedCounts:Formal class 'dgCMatrix' [package "Matrix"] with 6 slots
#> .. .. ..$ observed : num [1:1292193] 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1 ...
#> .. .. ..$ normalizer : num [1:1292193] 2.73 2.82 2.78 2.48 4.4 ...
#> .. .. ..$ expected : num 0.0596
#> $ 2R_2R:Formal class 'ContactMatrix' [package "InteractionSet"] with 5 slots
#> .. ..@ matrix :Formal class 'dgCMatrix' [package "Matrix"] with 6 slots
#> .. ..@ anchor1 : int [1:5058] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
#> .. ..@ anchor2 : int [1:5058] 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 ...
#> .. ..@ regions :Formal class 'GRanges' [package "GenomicRanges"] with 7 slots
#> .. ..@ metadata:List of 10
#> .. .. ..$ name : chr "2R_2R"
#> .. .. ..$ type : chr "cis"
#> .. .. ..$ kind : chr "U"
#> .. .. ..$ symmetric : logi TRUE
#> .. .. ..$ resolution : num 5000
#> .. .. ..$ expected : num [1:2769177] 746 703 746 152 192 ...
#> .. .. ..$ removedCounts:Formal class 'dgCMatrix' [package "Matrix"] with 6 slots
#> .. .. ..$ observed : num [1:2769177] 374 368 614 95 131 420 18 17 26 332 ...
#> .. .. ..$ normalizer : num [1:2769177] 2.62 2.19 1.84 2.94 2.46 ...
#> .. .. ..$ mtx : chr "norm"
#> - attr(*, "resolution")= num 5000
#> - attr(*, "chromSize")= tibble [2 × 3] (S3: tbl_df/tbl/data.frame)
#> ..$ name : chr [1:2] "2L" "2R"
#> ..$ length : num [1:2] 23513712 25286936
#> ..$ dimension: num [1:2] 4703 5058
#> - attr(*, "matricesKind")= tibble [3 × 4] (S3: tbl_df/tbl/data.frame)
#> ..$ name : chr [1:3] "2L_2L" "2L_2R" "2R_2R"
#> ..$ type : chr [1:3] "cis" "trans" "cis"
#> ..$ kind : chr [1:3] "U" NA "U"
#> ..$ symmetric: logi [1:3] TRUE FALSE TRUE
#> - attr(*, "mtx")= chr "o/e"
#> - attr(*, "expected")= tibble [4,961 × 2] (S3: tbl_df/tbl/data.frame)
#> ..$ distance: num [1:4961] 1 5001 10001 15001 20001 ...
#> ..$ expected: num [1:4961] 733 689 377 257 191 ...
#>The list has the attributes described below. These attributes are accessible via:
attributes(HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst)
#> $names
#> [1] "2L_2L" "2L_2R" "2R_2R"
#>
#> $resolution
#> [1] 5000
#>
#> $chromSize
#> # A tibble: 2 × 3
#> name length dimension
#> <chr> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 2L 23513712 4703
#> 2 2R 25286936 5058
#>
#> $matricesKind
#> # A tibble: 3 × 4
#> name type kind symmetric
#> <chr> <chr> <chr> <lgl>
#> 1 2L_2L cis U TRUE
#> 2 2L_2R trans NA FALSE
#> 3 2R_2R cis U TRUE
#>
#> $mtx
#> [1] "o/e"
#>
#> $expected
#> # A tibble: 4,961 × 2
#> distance expected
#> <dbl> <dbl>
#> 1 1 733.
#> 2 5001 689.
#> 3 10001 377.
#> 4 15001 257.
#> # ℹ 4,957 more rows
#>- names : the names of list elements (ContactMatrix).
-
resolution : the resolution of the HiC map.
-
chromSize : the size of the chromosomes in the
tibble format.
- seqnames : the sequence name (chromosome name).
- seqlengths : the sequence length in base pairs.
- dimension : the sequence length in number of bins. -
matricesKind : the kind of matrix that composes the
list in the tibble format.
- name : the matrix name. - type : interactionType. “Cis” for interactions on the same chromosome and “Trans” for interactions on different chromosomes. - kind : the matrix kind. U for upper triangle matrices, L for lower triangle matrices, NA for rectangular or square matrices. - symmetric : a boolean that indicates whether the matrix is symmetric (lower triangle identical to upper triangle).
- mtx : the kind of values in matrix. For exemple observed counts, normalized counts, observed/expected, etc.
-
expected : This attribute is related to the
OverExpectedHiCfunction. It gives a tibble with the expected counts as a function of genomic distance.
Each contactmatrix in the list have metadata. These are accessible via:
str(S4Vectors::metadata(HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst[["2L_2L"]]))
#> List of 10
#> $ name : chr "2L_2L"
#> $ type : chr "cis"
#> $ kind : chr "U"
#> $ symmetric : logi TRUE
#> $ resolution : num 5000
#> $ expected : num [1:2410023] 719 673 719 370 673 ...
#> $ removedCounts:Formal class 'dgCMatrix' [package "Matrix"] with 6 slots
#> .. ..@ i : int [1:266585] 2 10 18 19 20 28 32 37 38 40 ...
#> .. ..@ p : int [1:4704] 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0 ...
#> .. ..@ Dim : int [1:2] 4703 4703
#> .. ..@ Dimnames:List of 2
#> .. .. ..$ : NULL
#> .. .. ..$ : NULL
#> .. ..@ x : num [1:266585] 1 1 1 2 1 1 1 1 1 2 ...
#> .. ..@ factors : list()
#> $ observed : num [1:2410023] 1329 1721 1852 1076 2191 ...
#> $ normalizer : num [1:2410023] 1.399 1.115 0.888 1.139 0.908 ...
#> $ mtx : chr "norm"
#>- name : the name of the ContactMatrix.
-
type : interactionType. “Cis” for
interactions on the same chromosome and “Trans” for
interactions on different chromosomes (or arms).
- kind : the matrix kind. U for upper triangle matrices, L for lower triangle matrices, NA for rectangular or square
-
symmetric : a boolean that indicates whether the
matrix is symmetric (lower triangle identical to upper triangle).
- resolution : resolution of the HiC map.
-
removedCounts : A sparse matrix (dgCMatrix) of the
removed counts (counts that are below the threshold on rows or columns
as described in
BalanceHiC). - observed : observed counts of the sparse matrix.
-
normalizer : the balancer vector that converts the
observed counts into normalized counts. (observed * normalizer =
normalized counts).
- mtx : the kind of values in matrix. For example observed counts, normalized counts, observed/expected, etc.
-
expected : This attributes is related to the
OverExpectedHiCfunction. It gives the expected vector that convert the normalized counts into the observed/expected counts (normalized counts / expected = observed/expected).
Indexing
This part of the data corresponds to the positioning data (ChIPseq peaks, genomic features and annotations, genes, etc) on the genome. To integrate such annotations with HiC data in 2D matrices, annotations must be processed as followed.
The first step is the indexing of the features. It allows the features to be splitted and grouped into bins corresponding to the HiC bin size.
Example 1: Anchors from Beaf32 ChIP-seq peaks (bed file)
anchors_Index.gnr <- IndexFeatures(
gRangeList = list(Beaf=Beaf32_Peaks.gnr),
genomicConstraint = TADs_Domains.gnr,
chromSizes = chromSizes,
binSize = binSize,
metadataColName = "score",
method = "max"
)View
| seqnames | start | end | width | strand | name | bin | constraint | Beaf.score | Beaf.name | Beaf.bln |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 70001 | 75000 | 5000 | * | 2L:15:Tad_1 | 2L:15 | Tad_1 | 205 | Beaf32_8 | TRUE |
| 2L | 100001 | 105000 | 5000 | * | 2L:21:Tad_2 | 2L:21 | Tad_2 | 1830 | Beaf32_11 | TRUE |
| 2L | 110001 | 115000 | 5000 | * | 2L:23:Tad_3 | 2L:23 | Tad_3 | 1707 | Beaf32_14 | TRUE |
Example 2: Baits from TSS (transcription start sites from UCSC)
baits_Index.gnr <- IndexFeatures(
gRangeList = list(Tss=TSS_Peaks.gnr),
genomicConstraint = TADs_Domains.gnr,
chromSizes = chromSizes,
binSize = binSize,
metadataColName = "score",
method = "max"
)View
| seqnames | start | end | width | strand | name | bin | constraint | Tss.class | Tss.name | Tss.bln |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 75001 | 80000 | 5000 | * | 2L:16:Tad_1 | 2L:16 | Tad_1 | inactive | FBgn0031214 | TRUE |
| 2L | 105001 | 110000 | 5000 | * | 2L:22:Tad_3 | 2L:22 | Tad_3 | active | FBgn0026…. | TRUE |
| 2L | 115001 | 120000 | 5000 | * | 2L:24:Tad_3 | 2L:24 | Tad_3 | active | FBgn0031219 | TRUE |
Filter indexed features:
By using features names and bin IDs, it is possible to filter a subset of features. Example: Subset TSS that are not in the same bin than a Beaf32 peak.
non_Overlaps.ndx <- match(baits_Index.gnr$bin,
anchors_Index.gnr$bin, nomatch=0L)==0L
baits_Index.gnr <- baits_Index.gnr[non_Overlaps.ndx,]View
| seqnames | start | end | width | strand | name | bin | constraint | Tss.class | Tss.name | Tss.bln |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 75001 | 80000 | 5000 | * | 2L:16:Tad_1 | 2L:16 | Tad_1 | inactive | FBgn0031214 | TRUE |
| 2L | 105001 | 110000 | 5000 | * | 2L:22:Tad_3 | 2L:22 | Tad_3 | active | FBgn0026…. | TRUE |
| 2L | 115001 | 120000 | 5000 | * | 2L:24:Tad_3 | 2L:24 | Tad_3 | active | FBgn0031219 | TRUE |
Tips
- It is possible to index multiple features at the same time by
submitting a named list of GRanges. Names given in the list of GRanges
can then be used to filter indexed features and pairs.
- If genomicConstraint is defined, then anchors and baits will be
paired when located within the same region only. If contraint.gnr is
NULL, entire chromosomes (or arms) are used as constraints.
- When multiple ranges are in a same bin (ex: 3 ChIP-seq peaks in the
same 10kb bin), associated numeric variables in metadata
(
metadataColName) can be summarized according to the defined method (method), Example: Max peak score of the bin is kept in metadata columnscore.
Search Pairs
Pairing
SearchPairs function takes as input one or two indexed
features and returns all putative pairs within the same constraint (ex:
wihtin the same TAD).
If only one indexed features is defined in indexAnchor,
SearchPairs will return symetrical homotypic pairs
(A<->A), if indexAnchor and indexBait are defined, it will return
asymetrical heterotypic pairs (A<->B).
interactions.gni <- SearchPairs(
indexAnchor = anchors_Index.gnr,
indexBait = baits_Index.gnr
)View
| seq | start | end | seq | start | end | name | constraint | distance | orientation | submatrix.name | name | bin | Beaf.name | Beaf.score | Beaf.bln | name | bin | Tss.name | Tss.class | Tss.bln |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 70001 | 75000 | 2L | 75001 | 80000 | 2L:15_2L:16 | Tad_1 | 5000 | TRUE | 2L:15_2L:16 | 2L:15:Tad_1 | 2L:15 | Beaf32_8 | 205 | TRUE | 2L:16:Tad_1 | 2L:16 | FBgn0031214 | inactive | TRUE |
| 2L | 110001 | 115000 | 2L | 105001 | 110000 | 2L:23_2L:22 | Tad_3 | 5000 | FALSE | 2L:22_2L:23 | 2L:23:Tad_3 | 2L:23 | Beaf32_14 | 1707 | TRUE | 2L:22:Tad_3 | 2L:22 | FBgn0026…. | active | TRUE |
| 2L | 120001 | 125000 | 2L | 105001 | 110000 | 2L:25_2L:22 | Tad_3 | 15000 | FALSE | 2L:22_2L:25 | 2L:25:Tad_3 | 2L:25 | Beaf32_15 | 484 | TRUE | 2L:22:Tad_3 | 2L:22 | FBgn0026…. | active | TRUE |
Extractions
Case 1: Long-range interactions between two distal anchors.
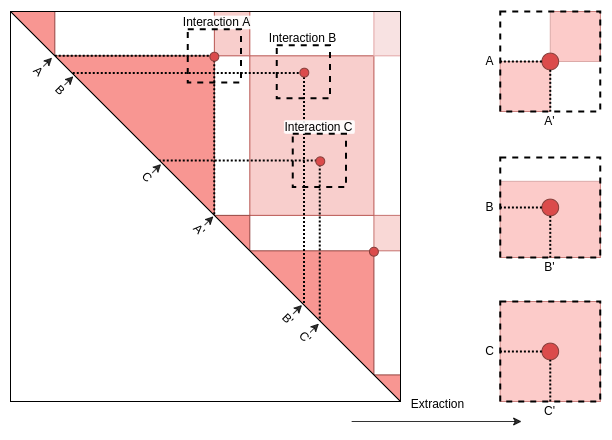
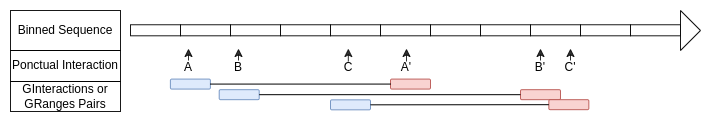
Interactions defined with GInteraction or Pairs of GRanges.
In extracted matrices, the middle of the Y axis corresponds to the center of the first element and interacts with the center of second element in the middle of the X axis.
interactions_PFmatrix.lst <- ExtractSubmatrix(
genomicFeature = interactions.gni,
hicLst = HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst,
referencePoint = "pf",
matriceDim = 41
)Interactions defined with GRanges.
The middle of the Y axis corresponds to the start of the range and interacts with the middle of the X axis which corresponds to the end of the range.
domains_PFmatrix.lst <- ExtractSubmatrix(
genomicFeature = TADs_Domains.gnr,
hicLst = HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst,
referencePoint = "pf",
matriceDim = 41
)Case 2: Interactions around genomic regions or domains.
In this case, extracted matrices are resized and scaled in order to fit all regions into the same area.
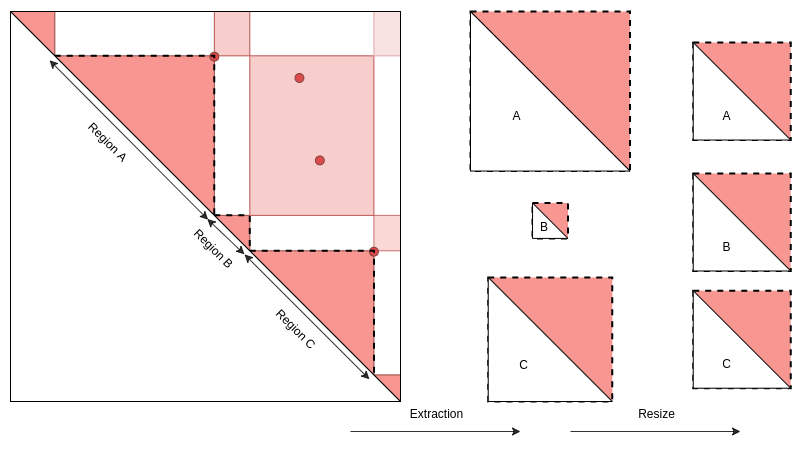
Regions defined with GInteraction object or Pairs of GRanges
The region’s start is defined by the center of the first element and
the region’s end by the center of the second element. 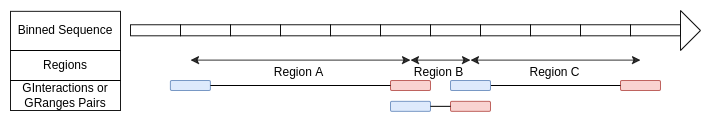
interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <- ExtractSubmatrix(
genomicFeature = interactions.gni,
hicLst = HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst,
hicResolution = NULL,
referencePoint = "rf",
matriceDim = 101
)Regions defined with GRanges
The regions are directly defined by the ranges of GRanges object.
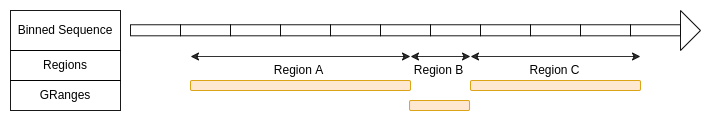
domains_RFmatrix.lst <- ExtractSubmatrix(
genomicFeature = TADs_Domains.gnr,
hicLst = HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst,
referencePoint = "rf",
matriceDim = 101,
cores = 1,
verbose = FALSE
)Case 3: Interactions along the chromosome axis.
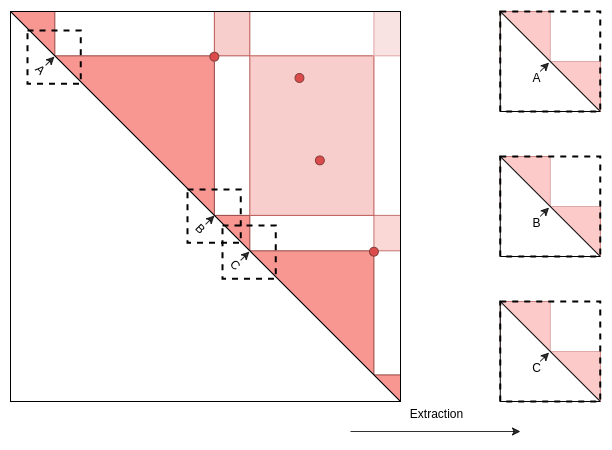
Example to analyse interactions in the context of TADs:
Step 1: generate a GRanges object of TAD boundaries by concatenating starts and ends of TADs.
domains_Border.gnr <- c(
GenomicRanges::resize(TADs_Domains.gnr, 1, "start"),
GenomicRanges::resize(TADs_Domains.gnr, 1, "end" )
) |>
sort()Step 2: Filter and reduce TAD boundaries GRanges object according to HiC resolution (binSize) + Store TAD names.
domains_Border_Bin.gnr <- BinGRanges(
gRange = domains_Border.gnr,
binSize = binSize,
verbose = FALSE
)
domains_Border_Bin.gnr$subname <- domains_Border_Bin.gnr$name
domains_Border_Bin.gnr$name <- domains_Border_Bin.gnr$bin
domains_Border_Bin.gnrView
| seq | start | end | strand | name | score | class | bin | subname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 70001 | 75000 | * | 2L:15 | 3 | active | 2L:15 | Tad_1 |
| 2L | 90001 | 95000 | * | 2L:19 | 3, 8 | active | 2L:19 | Tad_1, Tad_2 |
| 2L | 100001 | 105000 | * | 2L:21 | 8 | active | 2L:21 | Tad_2, Tad_3 |
Step 3: This defines a GRanges object. In the folowing examples, the same information is needed in a GInteraction object class.
domains_Border_Bin.gni <-
InteractionSet::GInteractions(
domains_Border_Bin.gnr,domains_Border_Bin.gnr)View
| seq | start | end | name | score | class | bin | subname | seq | start | end | name | score | class | bin | subname |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 70001 | 75000 | 2L:15 | 3 | active | 2L:15 | Tad_1 | 2L | 70001 | 75000 | 2L:15 | active | 3 | 2L:15 | Tad_1 |
| 2L | 90001 | 95000 | 2L:19 | 3, 8 | active | 2L:19 | Tad_1, Tad_2 | 2L | 90001 | 95000 | 2L:19 | active | 3, 8 | 2L:19 | Tad_1, Tad_2 |
| 2L | 100001 | 105000 | 2L:21 | 8 | active | 2L:21 | Tad_2, Tad_3 | 2L | 100001 | 105000 | 2L:21 | active | 8 | 2L:21 | Tad_2, Tad_3 |
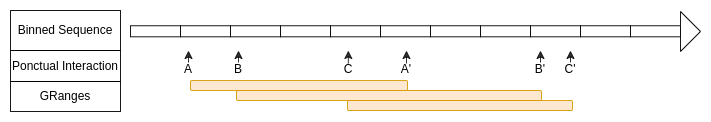
Ponctual interactions defined with GRanges
Here the start and the end of each ranges are in a same bin.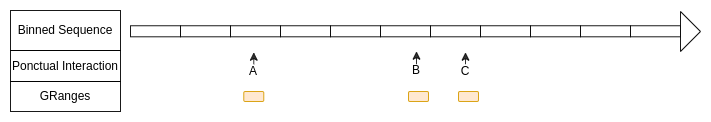
border_PFmatrix.lst <- ExtractSubmatrix(
genomicFeature = domains_Border_Bin.gnr,
hicLst = HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst,
referencePoint = "pf",
matriceDim = 101
)Ponctual interactions defined with GInteractions
Here the first (blue on scheme) and the second (red on scheme)
elements are the same. 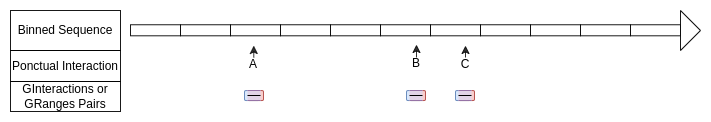
border_PFmatrix.lst <- ExtractSubmatrix(
genomicFeature = domains_Border_Bin.gni,
hicLst = HiC_Ctrl.cmx_lst,
referencePoint = "pf",
matriceDim = 101
)Filtrations
The modularity of the workflow allows the user to filter
interactions, pairs or extracted submatrices at any step of the
analysis. FilterInteractions function takes as input either
a GInteraction object or a list of submatrices, and a list of targets of
choice and a selectionFunction defining how targets are filtered.
Target list definition:
Target list must be defined by a named list corresponding to the same names of each element and correspond to the column of the GInteraction (or the attributes “interactions” of the matrices to be filtered). Then each element must be a character list to match this column or a function that will test each row in the column and return a bolean.
structureTarget.lst <- list(
first_colname_of_GInteraction = c("value"),
second_colname_of_GInteraction = function(eachElement){
min_th<value && value<max_th}
)Interactions, pairs or extracted submatrices are filtered by metadata
elements from GRanges objects used in SearchPairs. Those
metadata are stored in the attributes of the list of submatrices that
are accessible as follow:
attributes(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions
names(S4Vectors::mcols(attributes(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions))View
| seq | start | end | seq | start | end | name | constraint | distance | orientation | submatrix.name | name | bin | Beaf.name | Beaf.score | Beaf.bln | name | bin | Tss.name | Tss.class | Tss.bln |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2L | 120001 | 125000 | 2L | 105001 | 110000 | 2L:25_2L:22 | Tad_3 | 15000 | FALSE | 2L:22_2L:25 | 2L:25:Tad_3 | 2L:25 | Beaf32_15 | 484 | TRUE | 2L:22:Tad_3 | 2L:22 | FBgn0026…. | active | TRUE |
| 2L | 470001 | 475000 | 2L | 420001 | 425000 | 2L:95_2L:85 | Tad_17 | 50000 | FALSE | 2L:85_2L:95 | 2L:95:Tad_17 | 2L:95 | Beaf32_62 | 37 | TRUE | 2L:85:Tad_17 | 2L:85 | FBgn0031253 | active | TRUE |
| 2L | 470001 | 475000 | 2L | 450001 | 455000 | 2L:95_2L:91 | Tad_17 | 20000 | FALSE | 2L:91_2L:95 | 2L:95:Tad_17 | 2L:95 | Beaf32_62 | 37 | TRUE | 2L:91:Tad_17 | 2L:91 | FBgn0015924 | active | TRUE |
| 2L | 2490001 | 2495000 | 2L | 2530001 | 2535000 | 2L:499_2L:507 | Tad_64 | 40000 | TRUE | 2L:499_2L:507 | 2L:499:Tad_64 | 2L:499 | Beaf32_204 | 231 | TRUE | 2L:507:Tad_64 | 2L:507 | FBgn0264943 | inactive | TRUE |
| 2L | 2675001 | 2680000 | 2L | 2650001 | 2655000 | 2L:536_2L:531 | Tad_67 | 25000 | FALSE | 2L:531_2L:536 | 2L:536:Tad_67 | 2L:536 | Beaf32_210 | 124 | TRUE | 2L:531:Tad_67 | 2L:531 | FBgn0031442 | inactive | TRUE |
| 2L | 2800001 | 2805000 | 2L | 2770001 | 2775000 | 2L:561_2L:555 | Tad_70 | 30000 | FALSE | 2L:555_2L:561 | 2L:561:Tad_70 | 2L:561 | Beaf32_227 | 185 | TRUE | 2L:555:Tad_70 | 2L:555 | FBgn0019…. | active | TRUE |
| 2L | 2805001 | 2810000 | 2L | 2770001 | 2775000 | 2L:562_2L:555 | Tad_70 | 35000 | FALSE | 2L:555_2L:562 | 2L:562:Tad_70 | 2L:562 | Beaf32_227 | 185 | TRUE | 2L:555:Tad_70 | 2L:555 | FBgn0019…. | active | TRUE |
| 2L | 2975001 | 2980000 | 2L | 2990001 | 2995000 | 2L:596_2L:599 | Tad_76 | 15000 | TRUE | 2L:596_2L:599 | 2L:596:Tad_76 | 2L:596 | Beaf32_244 | 98 | TRUE | 2L:599:Tad_76 | 2L:599 | FBgn0025681 | active | TRUE |
| 2L | 3345001 | 3350000 | 2L | 3330001 | 3335000 | 2L:670_2L:667 | Tad_86 | 15000 | FALSE | 2L:667_2L:670 | 2L:670:Tad_86 | 2L:670 | Beaf32_2…. | 179 | TRUE | 2L:667:Tad_86 | 2L:667 | FBgn0031523 | inactive | TRUE |
| 2L | 3350001 | 3355000 | 2L | 3330001 | 3335000 | 2L:671_2L:667 | Tad_86 | 20000 | FALSE | 2L:667_2L:671 | 2L:671:Tad_86 | 2L:671 | Beaf32_281 | 100 | TRUE | 2L:667:Tad_86 | 2L:667 | FBgn0031523 | inactive | TRUE |
Example of target list:
In this example, Pairs will be filtered on anchor.Beaf.name, bait.Tss.name, name (which correponds to the submatrix IDs) and distance. The aim of the example is to filter Pairs or submatrices that have:
- “Beaf32_62” and “Beaf32_204” in
anchor.Beaf.name
- “FBgn0015924” and “FBgn0264943” in
bait.Tss.name
- distance exactly equal to 20000 or 40000 And to exclude Pairs or submatrices that have:
- “2L:25_2L:22” in name
Selection Function definition:
The selectionFunction defines which operations (union(), intersect(), setdiff()…) are used to filter the set of Pairs with target elements. For more examples, see Selection function tips and examples section.
Filtration with selection
Example of GInteraction object filtration
With a GInteraction object as input, FilterInteractions
will return the indices of filtered elements.
With the targets and selectionFun defined above:
FilterInteractions(
genomicInteractions =
attributes(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions,
targets = targets,
selectionFun = selectionFun
)
#> [1] 3 4Example of Matrices list filtration
With a matrices list as input, FilterInteractions will
return the filtered matrices list, with updated attributes.
With the targets and selectionFun defined above:
filtred_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <- FilterInteractions(
matrices = interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
targets = targets,
selectionFun = selectionFun
)Specific case 1: Only one target (and therefore no selection needed)
For example, to filter the top 100 first elements, select the top 100 first names
GInteraction filtration
FilterInteractions(
genomicInteractions =
attributes(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions,
targets = first100_targets,
selectionFun = NULL
) |> head()
#> submatrix.name1 submatrix.name2 submatrix.name3 submatrix.name4 submatrix.name5
#> 1 2 3 4 5
#> submatrix.name6
#> 6Matrices list filtration
first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <- FilterInteractions(
matrices = interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
targets = first100_targets,
selectionFun = NULL
)
attributes(first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions
#> GInteractions object with 100 interactions and 15 metadata columns:
#> seqnames1 ranges1 seqnames2 ranges2 |
#> <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> <IRanges> |
#> 2L:25_2L:22 2L 120001-125000 --- 2L 105001-110000 |
#> 2L:95_2L:85 2L 470001-475000 --- 2L 420001-425000 |
#> 2L:95_2L:91 2L 470001-475000 --- 2L 450001-455000 |
#> 2L:499_2L:507 2L 2490001-2495000 --- 2L 2530001-2535000 |
#> 2L:536_2L:531 2L 2675001-2680000 --- 2L 2650001-2655000 |
#> ... ... ... ... ... ... .
#> 2L:4313_2L:4299 2L 21560001-21565000 --- 2L 21490001-21495000 |
#> 2L:4315_2L:4299 2L 21570001-21575000 --- 2L 21490001-21495000 |
#> 2L:4312_2L:4305 2L 21555001-21560000 --- 2L 21520001-21525000 |
#> 2L:4313_2L:4305 2L 21560001-21565000 --- 2L 21520001-21525000 |
#> 2L:4315_2L:4305 2L 21570001-21575000 --- 2L 21520001-21525000 |
#> name constraint distance orientation
#> <character> <character> <integer> <logical>
#> 2L:25_2L:22 2L:25_2L:22 Tad_3 15000 FALSE
#> 2L:95_2L:85 2L:95_2L:85 Tad_17 50000 FALSE
#> 2L:95_2L:91 2L:95_2L:91 Tad_17 20000 FALSE
#> 2L:499_2L:507 2L:499_2L:507 Tad_64 40000 TRUE
#> 2L:536_2L:531 2L:536_2L:531 Tad_67 25000 FALSE
#> ... ... ... ... ...
#> 2L:4313_2L:4299 2L:4313_2L:4299 Tad_486 70000 FALSE
#> 2L:4315_2L:4299 2L:4315_2L:4299 Tad_486 80000 FALSE
#> 2L:4312_2L:4305 2L:4312_2L:4305 Tad_486 35000 FALSE
#> 2L:4313_2L:4305 2L:4313_2L:4305 Tad_486 40000 FALSE
#> 2L:4315_2L:4305 2L:4315_2L:4305 Tad_486 50000 FALSE
#> submatrix.name anchor.bin anchor.name bait.bin
#> <character> <character> <character> <character>
#> 2L:25_2L:22 2L:22_2L:25 2L:25 2L:25:Tad_3 2L:22
#> 2L:95_2L:85 2L:85_2L:95 2L:95 2L:95:Tad_17 2L:85
#> 2L:95_2L:91 2L:91_2L:95 2L:95 2L:95:Tad_17 2L:91
#> 2L:499_2L:507 2L:499_2L:507 2L:499 2L:499:Tad_64 2L:507
#> 2L:536_2L:531 2L:531_2L:536 2L:536 2L:536:Tad_67 2L:531
#> ... ... ... ... ...
#> 2L:4313_2L:4299 2L:4299_2L:4313 2L:4313 2L:4313:Tad_486 2L:4299
#> 2L:4315_2L:4299 2L:4299_2L:4315 2L:4315 2L:4315:Tad_486 2L:4299
#> 2L:4312_2L:4305 2L:4305_2L:4312 2L:4312 2L:4312:Tad_486 2L:4305
#> 2L:4313_2L:4305 2L:4305_2L:4313 2L:4313 2L:4313:Tad_486 2L:4305
#> 2L:4315_2L:4305 2L:4305_2L:4315 2L:4315 2L:4315:Tad_486 2L:4305
#> bait.name anchor.Beaf.score anchor.Beaf.name
#> <character> <numeric> <list>
#> 2L:25_2L:22 2L:22:Tad_3 484 Beaf32_15
#> 2L:95_2L:85 2L:85:Tad_17 37 Beaf32_62
#> 2L:95_2L:91 2L:91:Tad_17 37 Beaf32_62
#> 2L:499_2L:507 2L:507:Tad_64 231 Beaf32_204
#> 2L:536_2L:531 2L:531:Tad_67 124 Beaf32_210
#> ... ... ... ...
#> 2L:4313_2L:4299 2L:4299:Tad_486 748 Beaf32_1348
#> 2L:4315_2L:4299 2L:4299:Tad_486 529 Beaf32_1349
#> 2L:4312_2L:4305 2L:4305:Tad_486 748 Beaf32_1348
#> 2L:4313_2L:4305 2L:4305:Tad_486 748 Beaf32_1348
#> 2L:4315_2L:4305 2L:4305:Tad_486 529 Beaf32_1349
#> anchor.Beaf.bln bait.Tss.class bait.Tss.name
#> <logical> <list> <list>
#> 2L:25_2L:22 TRUE active FBgn0026787,FBgn0005278
#> 2L:95_2L:85 TRUE active FBgn0031253
#> 2L:95_2L:91 TRUE active FBgn0015924
#> 2L:499_2L:507 TRUE inactive FBgn0264943
#> 2L:536_2L:531 TRUE inactive FBgn0031442
#> ... ... ... ...
#> 2L:4313_2L:4299 TRUE inactive FBgn0053837
#> 2L:4315_2L:4299 TRUE inactive FBgn0053837
#> 2L:4312_2L:4305 TRUE inactive FBgn0053873
#> 2L:4313_2L:4305 TRUE inactive FBgn0053873
#> 2L:4315_2L:4305 TRUE inactive FBgn0053873
#> bait.Tss.bln
#> <logical>
#> 2L:25_2L:22 TRUE
#> 2L:95_2L:85 TRUE
#> 2L:95_2L:91 TRUE
#> 2L:499_2L:507 TRUE
#> 2L:536_2L:531 TRUE
#> ... ...
#> 2L:4313_2L:4299 TRUE
#> 2L:4315_2L:4299 TRUE
#> 2L:4312_2L:4305 TRUE
#> 2L:4313_2L:4305 TRUE
#> 2L:4315_2L:4305 TRUE
#> -------
#> regions: 335 ranges and 0 metadata columns
#> seqinfo: 2 sequences from an unspecified genomeWarning! A selection of some matrices removes attributes.
attributes(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst[1:20])$interactions
#> NULLSpecific case 2: Sampling
nSample.num = 3
set.seed(123)
targets = list(name=sample(
attributes(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions$name,nSample.num))GInteraction sampling
FilterInteractions(
genomicInteractions =
attributes(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions,
targets = targets,
selectionFun = NULL
)
#> name1 name2 name3
#> 14 50 118Matrices list sampling
sampled_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <- FilterInteractions(
matrices = interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
targets = targets,
selectionFun = NULL
)
attributes(sampled_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions
#> GInteractions object with 3 interactions and 15 metadata columns:
#> seqnames1 ranges1 seqnames2 ranges2 |
#> <Rle> <IRanges> <Rle> <IRanges> |
#> 2L:1012_2L:1015 2L 5055001-5060000 --- 2L 5070001-5075000 |
#> 2L:3002_2L:2978 2L 15005001-15010000 --- 2L 14885001-14890000 |
#> 2R:1824_2R:1820 2R 9115001-9120000 --- 2R 9095001-9100000 |
#> name constraint distance orientation
#> <character> <character> <integer> <logical>
#> 2L:1012_2L:1015 2L:1012_2L:1015 Tad_132 15000 TRUE
#> 2L:3002_2L:2978 2L:3002_2L:2978 Tad_356 120000 FALSE
#> 2R:1824_2R:1820 2R:1824_2R:1820 Tad_608 20000 FALSE
#> submatrix.name anchor.bin anchor.name bait.bin
#> <character> <character> <character> <character>
#> 2L:1012_2L:1015 2L:1012_2L:1015 2L:1012 2L:1012:Tad_132 2L:1015
#> 2L:3002_2L:2978 2L:2978_2L:3002 2L:3002 2L:3002:Tad_356 2L:2978
#> 2R:1824_2R:1820 2R:1820_2R:1824 2R:1824 2R:1824:Tad_608 2R:1820
#> bait.name anchor.Beaf.score anchor.Beaf.name
#> <character> <numeric> <list>
#> 2L:1012_2L:1015 2L:1015:Tad_132 660 Beaf32_374,Beaf32_375
#> 2L:3002_2L:2978 2L:2978:Tad_356 49 Beaf32_1001
#> 2R:1824_2R:1820 2R:1820:Tad_608 977 Beaf32_1734
#> anchor.Beaf.bln bait.Tss.class bait.Tss.name bait.Tss.bln
#> <logical> <list> <list> <logical>
#> 2L:1012_2L:1015 TRUE active FBgn0261608 TRUE
#> 2L:3002_2L:2978 TRUE inactive FBgn0266840 TRUE
#> 2R:1824_2R:1820 TRUE active FBgn0082927 TRUE
#> -------
#> regions: 335 ranges and 0 metadata columns
#> seqinfo: 2 sequences from an unspecified genomeSpecific case 3: Filtration without selectionFunction
Without any selectionFunction, FilterInteractions will
return all indices corresponding to each target in the list. Then, the
indices of interest can be selected in a second step. For the examples
we take the folowing targets:
targets <- list(
anchor.Beaf.name = c("Beaf32_8","Beaf32_15"),
bait.Tss.name = c("FBgn0031214","FBgn0005278"),
name = c("2L:74_2L:77"),
distance = function(columnElement){
return(14000==columnElement || columnElement == 3000)
}
)GInteraction filtration
FilterInteractions(
genomicInteractions =
attributes(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions,
targets = targets,
selectionFun = NULL
) |> str()
#> List of 4
#> $ anchor.Beaf.name: int 1
#> $ bait.Tss.name : int 1
#> $ name : int(0)
#> $ distance : int(0)Matrices list filtration
FilterInteractions(
matrices = interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
targets = targets,
selectionFun = NULL
) |>
str()
#> List of 4
#> $ anchor.Beaf.name: int 1
#> $ bait.Tss.name : int 1
#> $ name : int(0)
#> $ distance : int(0)Tips
- Filter a GInteraction object allows to intersect the selected
index.
- Filter a matrices list without selection is better than filter the interaction attributes of the matrices list
Selection function tips and examples:
- What is common to A, B and C
- What is in A and/or B and/or C
- What is only in A
- What is common in A with B, and not in C
- What is common in A with B, plus all that is present in C
- What is common in C with all elements present in A and B
- Everything that is present in A and B but not in C
- What is present only once
d <- c(a,b,c)
setdiff(d,d[duplicated(d)]) |> sort()
#> [1] "D" "E" "F"Orientation
ExtractSubmatrix returns submatrices orientated
according to 5’->3’ orientation of the chromosome. In the case of
heterotypic or asymetric pairs (anchor != bait), anchors and baits are
thus mixed on Y and X axis of the matrices.
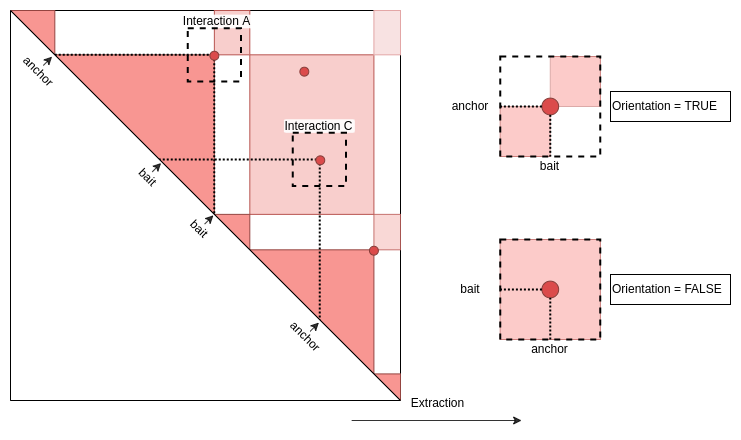
OrientateMatrix function allows to force all matrices to
be orientated in a way that anchors will be systematically on Y axis and
baits on X axis.
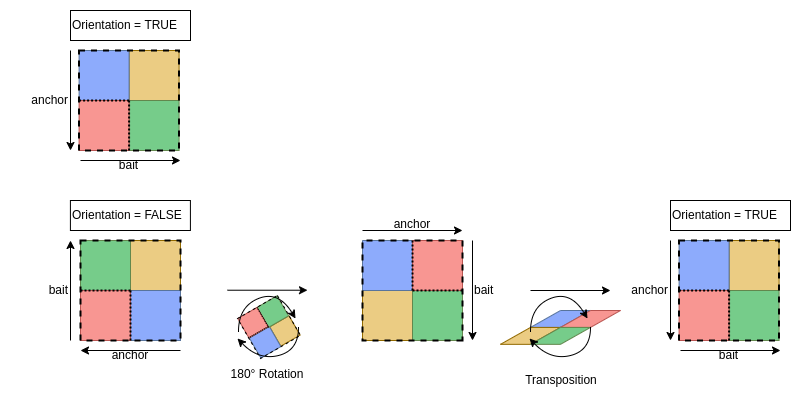
Information about the orientation
# mcols(attributes(
# first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)$interactions)$orientation- The 13th matrice is well oriented, i.e. the anchor Beaf is
in Y axis and the bait TSS in X axis
- The 14th matrice is not well oriented, i.e. the bait TSS is in Y axis and the anchor Beaf in X axis
Orientation on matrices list
oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <-
OrientateMatrix(first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)
#> 69 matrices are orientedOrientation of one matrix only.
Warning This procedure force orientation even if not needed.
orientedMatrix.mtx <-
OrientateMatrix(first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst[[1]])Prepare matrices list
PrepareMtxList can be used to perform operations on the
matrices list. This function prepares the matrices list by performing a
per matrix operation by transforming values. For example values can be
quantilized inorder to rank local interactions and highlight on the
contacts with the highest values. This function can also be used to
correct orientations, just as OrientateMatrix. The reason
for giving access for the user to this originally hidden function is to
have a uniformly prepared matrices list for both quantifications and
visualisations.
oriented_quantiled_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <-
PrepareMtxList(
first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
transFun = 'quantile',
orientate = TRUE)
#> 69 matrices are oriented
oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <-
PrepareMtxList(
first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
orientate = TRUE)
#> 69 matrices are orientedQuantifications
GetQuantif function takes as input a list of submatrices
and returns a vector of contact frequencies in a given typeof regions
where these contacts are computed with a function.
Basic quantifications
The GetQuantif function extracts per submatrix the
average values of the 3*3 central pixels by default (see
GetQuantif).
- area: The region where the contacts values are extracted in each matrix.
- operation The function that is done on extracted values for each matrix.
Example: Average of the values in the centered 3x3 square.
center.num <- GetQuantif(
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
areaFun = "center",
operationFun = "mean"
)Custom functions
The GetQuantif function also takes custom
area and operation in parameter.
-
area: function defining on which submatrix
coordinates the values are extracted in each matrices.
- operation function defining which operation is done on extracted values for each matrices.
Example: Interactions values on the matrice.mtx[33:35,67:69] area, averaged after removing all zeros.
GetQuantif(
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
areaFun = function(matrice.mtx){matrice.mtx[33:35,67:69]},
operationFun = function(area.mtx){
area.mtx[which(area.mtx==0)]<-NA;
return(mean(area.mtx,na.rm=TRUE))
}
) |>
c() |>
unlist() |>
head()
#> 2L:25_2L:22 2L:95_2L:85 2L:95_2L:91 2L:499_2L:507 2L:536_2L:531
#> 1.2652268 1.0275631 1.8478690 0.8648371 1.1975185
#> 2L:561_2L:555
#> 1.6126441Particular cases:
Values naming
By default, returned values are named with submatrix ID. If
varName is set with an element metadata column name from
GInteraction attributes, values are returned values are named according
to this element.
Example: Named quantifications with anchor.Beaf.name
namedCenter.num <- GetQuantif(
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
areaFun = "center",
operationFun = "mean",
varName = "anchor.Beaf.name"
)Note that changing submatrix ID for other names can create name duplicates:
Example: The 46th matrix is correspond to two Beaf32 peaks, i.e. it has two anchor.Beaf.name
| name | anchor.Beaf.name | |
|---|---|---|
| 45 | 2L:2676_2L:2680 | Beaf32_950 |
| 46 | 2L:2768_2L:2765 | Beaf32_981 |
| 47 | 2L:2971_2L:2977 | Beaf32_1000 |
| 48 | 2L:3002_2L:2977 | Beaf32_1001 |
| 49 | 2L:2971_2L:2978 | Beaf32_1000 |
| 50 | 2L:3002_2L:2978 | Beaf32_1001 |
As a consequence, the value in center.num is duplicated in namedCenter.num
unlist(c(center.num))[45:50]
#> 2L:2676_2L:2680 2L:2768_2L:2765 2L:2971_2L:2977 2L:3002_2L:2977 2L:2971_2L:2978
#> 0.7318490 0.8071858 0.5238616 0.7522744 0.5438497
#> 2L:3002_2L:2978
#> 0.7135216
unlist(c(namedCenter.num))[45:51]
#> Beaf32_378 Beaf32_408 Beaf32_408 Beaf32_408 Beaf32_437 Beaf32_518 Beaf32_521
#> 1.1762447 1.0476893 0.8868763 0.7318490 0.8071858 0.5238616 0.7522744Duplicated value index are stored in attributes.
attributes(center.num)$duplicated
#> NULL
attributes(namedCenter.num)$duplicated
#> NULLOne value extraction
GetQuantif(
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
areaFun = function(matrice.mtx){matrice.mtx[5,5]},
operationFun = function(area.mtx){area.mtx}
) |>
head()
#> 2L:25_2L:22 2L:95_2L:85 2L:95_2L:91 2L:499_2L:507 2L:536_2L:531
#> 1.6036209 1.2231158 1.2129980 0.8516612 0.3858703
#> 2L:561_2L:555
#> 0.8043792Area extraction
GetQuantif(
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
areaFun = function(matrice.mtx){matrice.mtx[4:6,4:6]},
operationFun = function(area){area}
) |>
head()
#> 2L:25_2L:22 2L:95_2L:85 2L:95_2L:91 2L:499_2L:507 2L:536_2L:531
#> 1.599228 NA NA 1.716875 1.603621
#> 2L:561_2L:555
#> NATips
- If
operationFunis NULL then it will return values of the selected region without NA.
GetQuantif(
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
areaFun = function(matrice.mtx){matrice.mtx[4:6,4:6]},
operationFun = NULL
) |>
head()
#> 2L:25_2L:22 2L:95_2L:85 2L:95_2L:91 2L:499_2L:507 2L:536_2L:531
#> 1.599228 1.716875 1.603621 1.834523 1.731368
#> 2L:561_2L:555
#> 1.628212Aggregations
Aggregation function takes as input a list of
submatrices and returns an aggregated matrix using the aggregation
function defined by the user.
One sample aggregation
Basic aggregation
Aggregation function has some default aggregation
functions like sum, mean or
median (see Aggregation)
# rm0 argument can be added to PrepareMtxList to assign NA to 0 values.
oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst =
PrepareMtxList(
oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
rm0 = FALSE)
agg_sum.mtx <- Aggregation(
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
aggFun = "sum"
)Custom aggregation
Defining a custom aggregation function: example below shows the mean function after removing NA.
agg_mean.mtx <- Aggregation(
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
aggFun = function(x){mean(x,na.rm=TRUE)}
)Two samples differential aggregation
Aggregation function can take as input two list of
submatrices from two samples or conditions and returns a differential
aggregated matrix. Two ways to obtain differential aggregation are
applied, first is by assessing differences on each individual pairs of
submatrices then aggregate the differences; second is by aggregating
matrices and assess differences on the aggregated matrices (see examples
below).
Preparation of matrices list
- Preparation of Control matrices list condition
Filtration
first100_targets = list(
submatrix.name = names(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)[1:100]
)
first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <- FilterInteractions(
matrices = interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
targets = first100_targets,
selectionFun = NULL
)Orientation
oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <-
OrientateMatrix(first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)- Preparation of second matrices list in Beaf depleted condition. Extraction
interactions_RFmatrix.lst <- ExtractSubmatrix(
genomicFeature = interactions.gni,
hicLst = HiC_HS.cmx_lst,
referencePoint = "rf",
matriceDim = 101
)Filtration
first100_interactions_RFmatrix.lst <- FilterInteractions(
matrices = interactions_RFmatrix.lst,
targets = first100_targets,
selectionFun = NULL
)Orientation
oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix.lst <-
OrientateMatrix(first100_interactions_RFmatrix.lst)
#> 69 matrices are orientedAggregate
oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst =
PrepareMtxList(first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
minDist = NULL,
maxDist = NULL,
rm0 = FALSE,
orientate = TRUE
)
#> 69 matrices are oriented
oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix.lst =
PrepareMtxList(first100_interactions_RFmatrix.lst,
minDist = NULL,
maxDist = NULL,
rm0 = FALSE,
orientate = TRUE
)
#> 69 matrices are oriented
diffAggreg.mtx <- Aggregation(
ctrlMatrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
matrices = oriented_first100_interactions_RFmatrix.lst,
aggFun = "mean",
diffFun = "substraction",
scaleCorrection = TRUE,
correctionArea = list(
i = c(1:30),
j = c(72:101)
),
statCompare = TRUE)Tips
On PrepareMtxList function:
-
PrepareMtxListacts as a one stop function to perform value treatment and orientation correction allowing to have consistent matrices list for both quantification and visualization process to come. - If
rm0isTRUEall zeros in matrices list will be replaced by NA. - It is possible to filter submatrices list by minimal or maximal distance during the aggregation function.
- It is possible to orientate submatrices at this point or using
OrientateMatrixfunction. -
PrepareMtxListkeeps former attributes matrices list and adds new ones:- totalMatrixNumber: total number of matrices.
- filteredMatrixNumber: number of matrices after distance
filtering.
- minimalDistance: minimal distance between anchor and bait.
- maximalDistance: maximal distance between anchor and bait.
- transformationMethod: the function used to perform a per matrix data transformation.
- zeroRemoved: A Boolean that indicates if zeros have been replaced by NA.
On Aggregation function:
- When aggregation is performed using one sample only, use either
matricesorctrlMatricesparameters - The
statComparemay not be setTRUEevery time (due to memory requirement). -
Aggregationon one sample keeps former attributes of the matrices list and add new ones:- aggregationMethod: The function applied to obtain the
aggregation.
- aggregationMethod: The function applied to obtain the
aggregation.
-
Aggregationon two samples adds additional attributes:- correctedFact: The value that is added to the condition to reduce noise. It’s computed as the median difference between condition and control in an background area (e.g upper right corner in matrices).
- matrices: The list of matrices.
- agg: Aggregation of the condition.
- aggCtrl: Aggregation of the control.
- aggCorrected: Aggregation of the condition corrected with correctedFact.
- aggDelta: the difference between the aggregated matrix of the
condition and the aggregated matrix of the control.
- aggCorrectedDelta: the difference between the aggregated matrix of the condition corrected with correctedFact and the aggregated matrix of the control.
- agg: Aggregation of the condition.
Aggregations plots
Preparation of aggregated matrices
- Control aggregation with no orientation
aggreg.mtx <- Aggregation(
ctrlMatrices=interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
aggFun="mean"
)- Control aggregation with orientation
oriented_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst <-
OrientateMatrix(interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst)
#> 95 matrices are oriented
orientedAggreg.mtx <- Aggregation(
ctrlMatrices=oriented_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
aggFun="mean"
)- Differential aggregation
oriented_interactions_RFmatrix.lst <-
OrientateMatrix(interactions_RFmatrix.lst)
#> 95 matrices are oriented
diffAggreg.mtx <- Aggregation(
ctrlMatrices = oriented_interactions_RFmatrix_ctrl.lst,
matrices = oriented_interactions_RFmatrix.lst,
aggFun = "mean",
diffFun = "log2+1",
scaleCorrection = TRUE,
correctionArea = list( i=c(1:30) , j=c(72:101) ),
statCompare = TRUE
)Plots
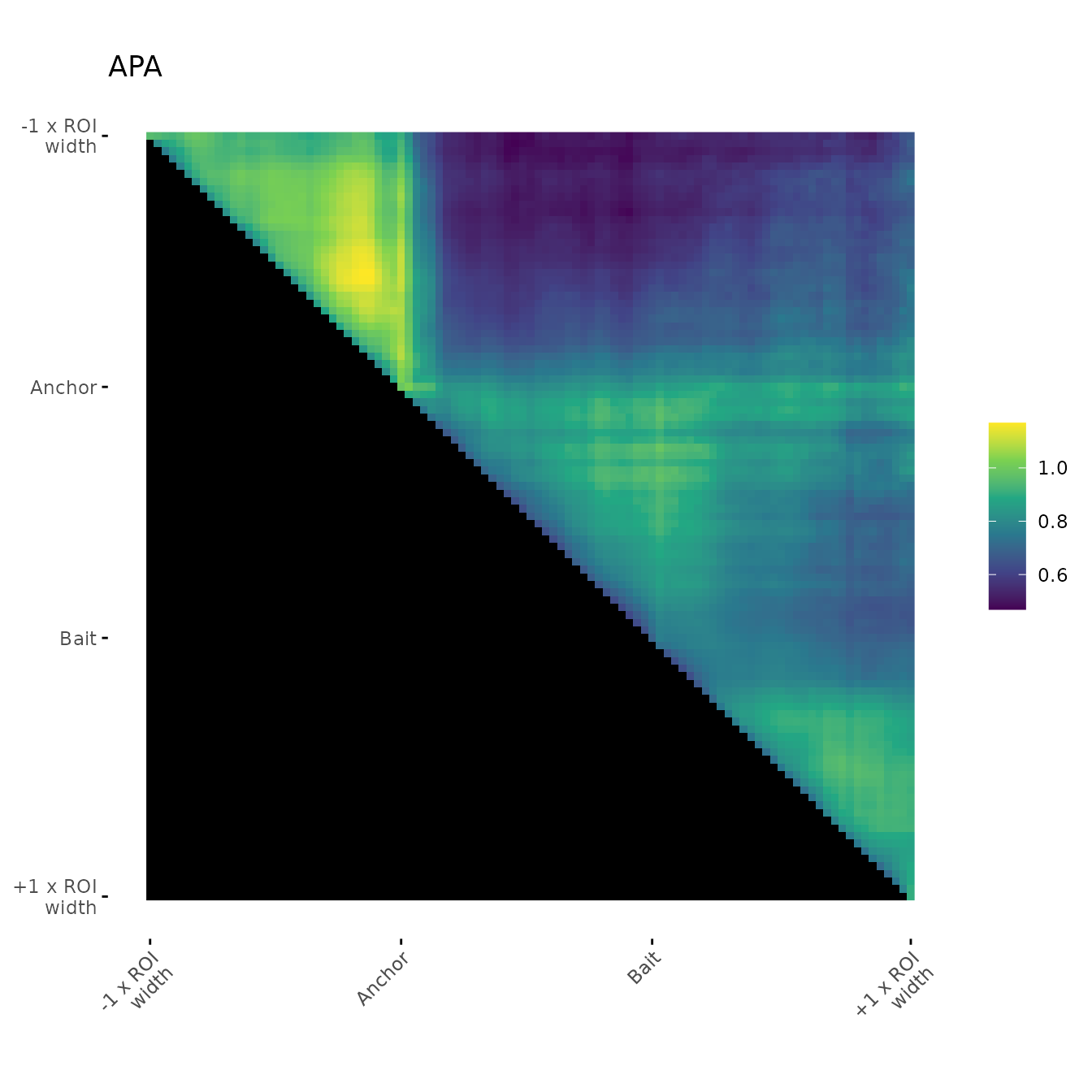
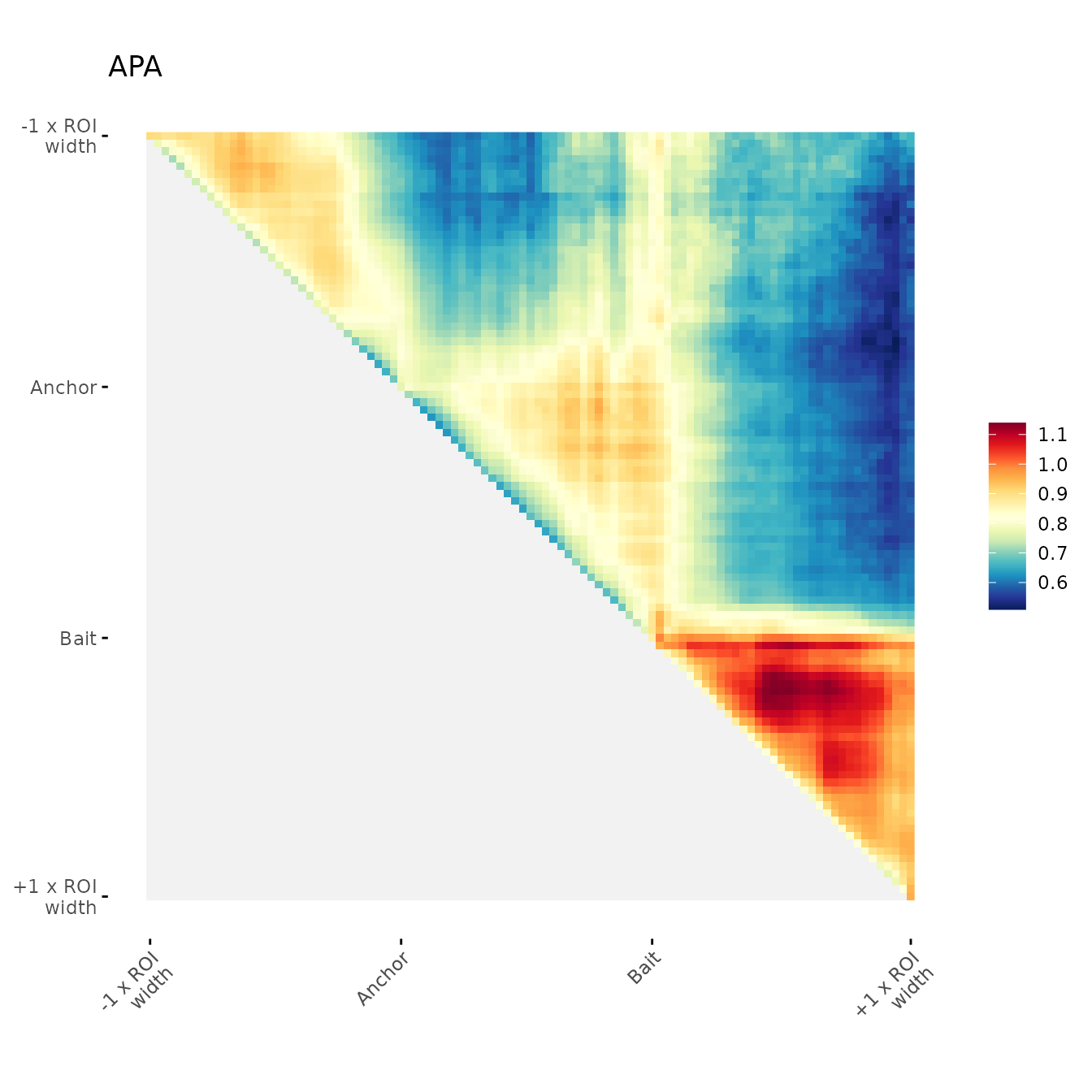
Simple aggregation plot:
With no orientation
ggAPA function creates a ggplot object
(ggplot2::geom_raster)
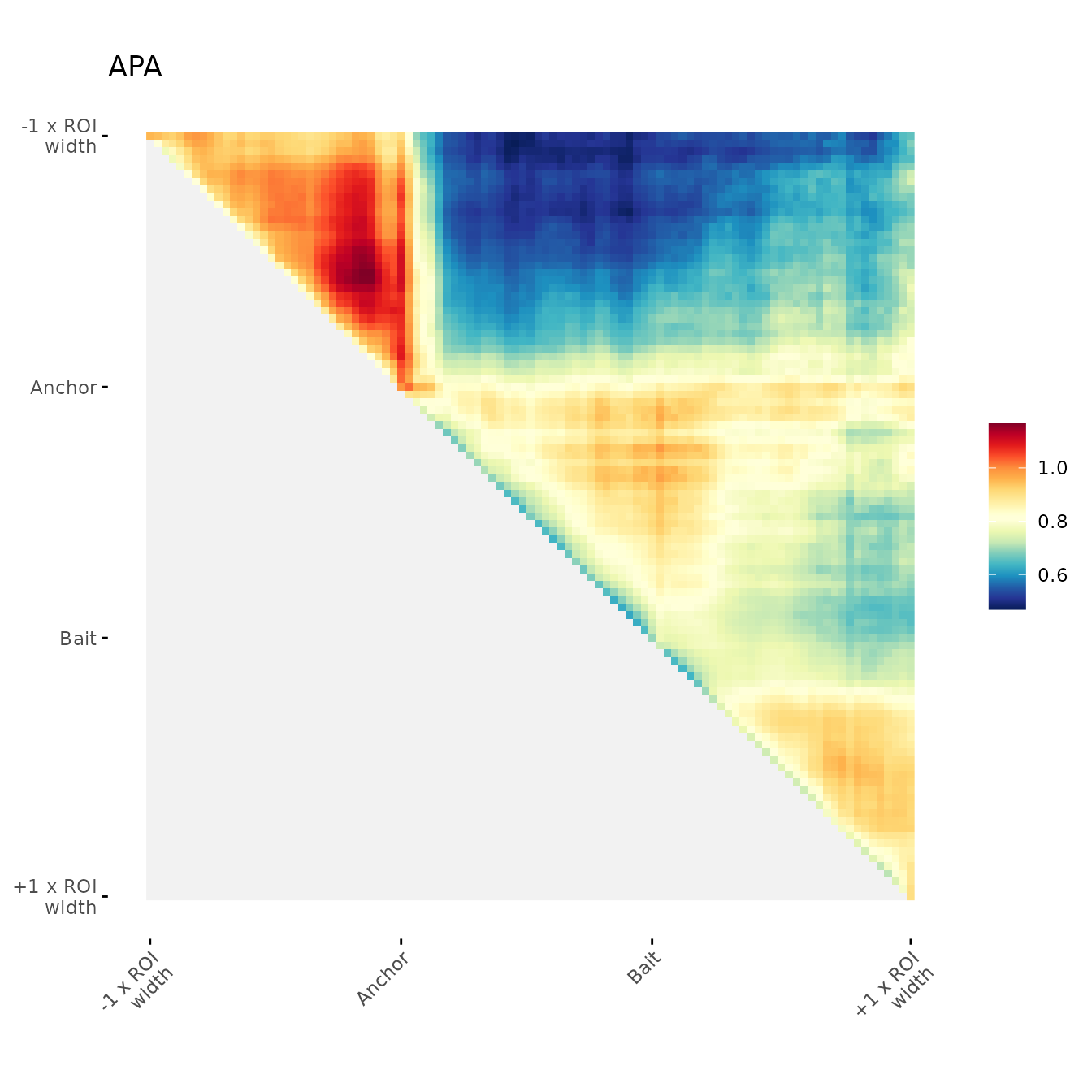
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = aggreg.mtx,
title = "APA"
)
Further visualisation parameters:
Trimming aggregated values for visualisation:
It is possible to set a specific range of values of the scale, for this remove a percentage of values using upper tail, lower tail or both tails of the distribution.
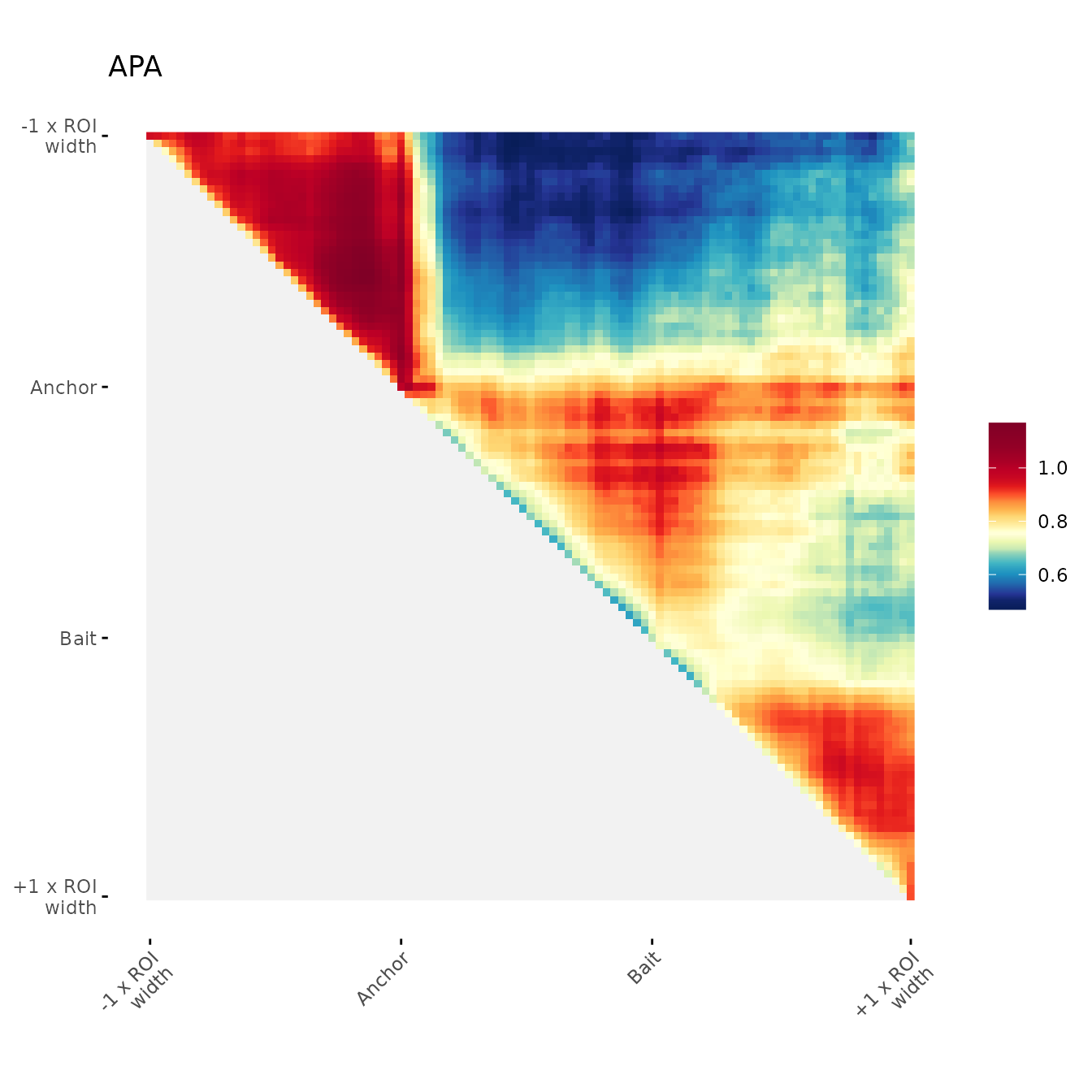
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA 30% trimmed on upper side",
trim = 30,
tails = "upper"
)
#> Warning in max(unlist(bounds.num_lst[1]), na.rm = TRUE): no non-missing
#> arguments to max; returning -Inf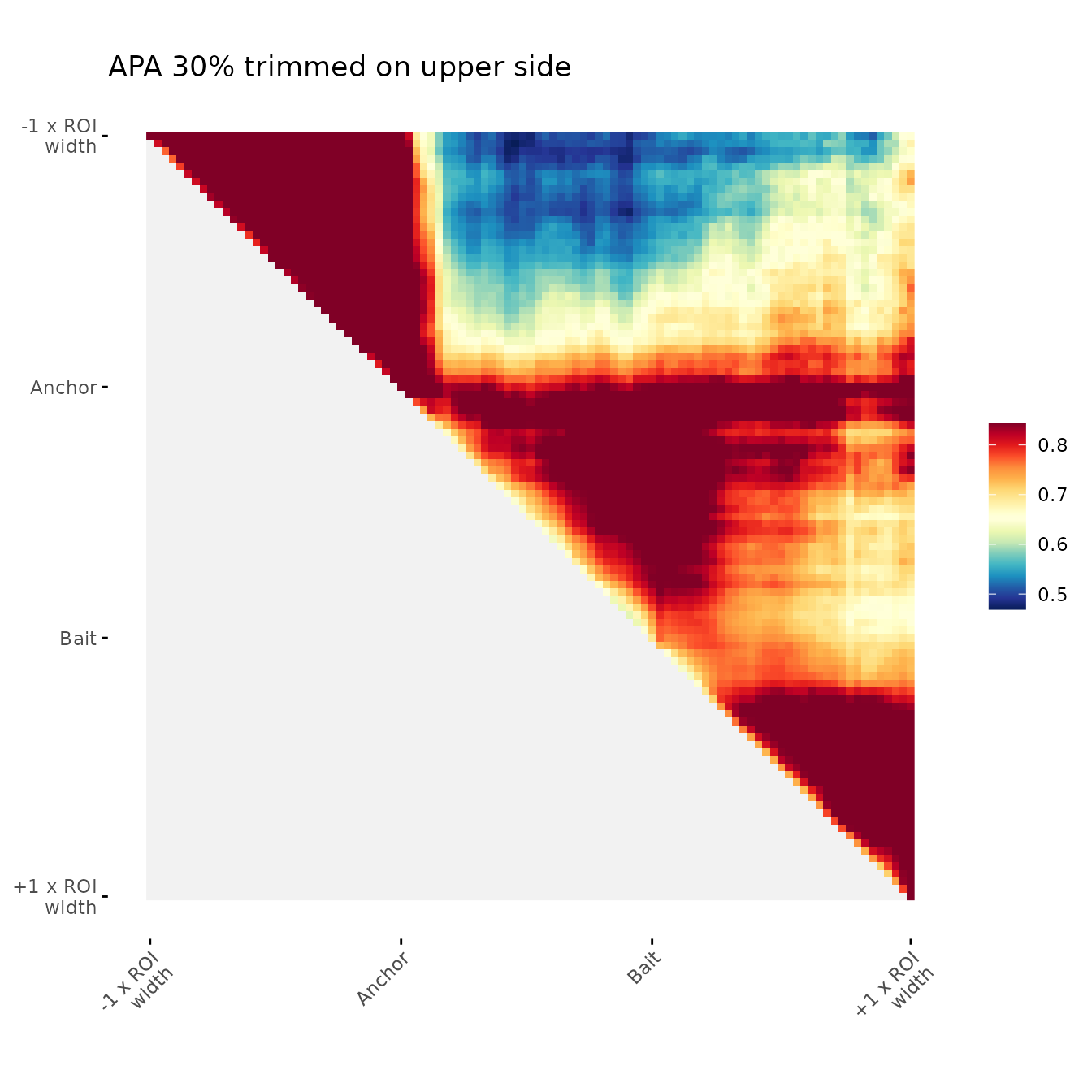
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA 30% trimmed on upper side",
trim = 30,
tails = "lower"
)
#> Warning in min(unlist(bounds.num_lst[2]), na.rm = TRUE): no non-missing
#> arguments to min; returning Inf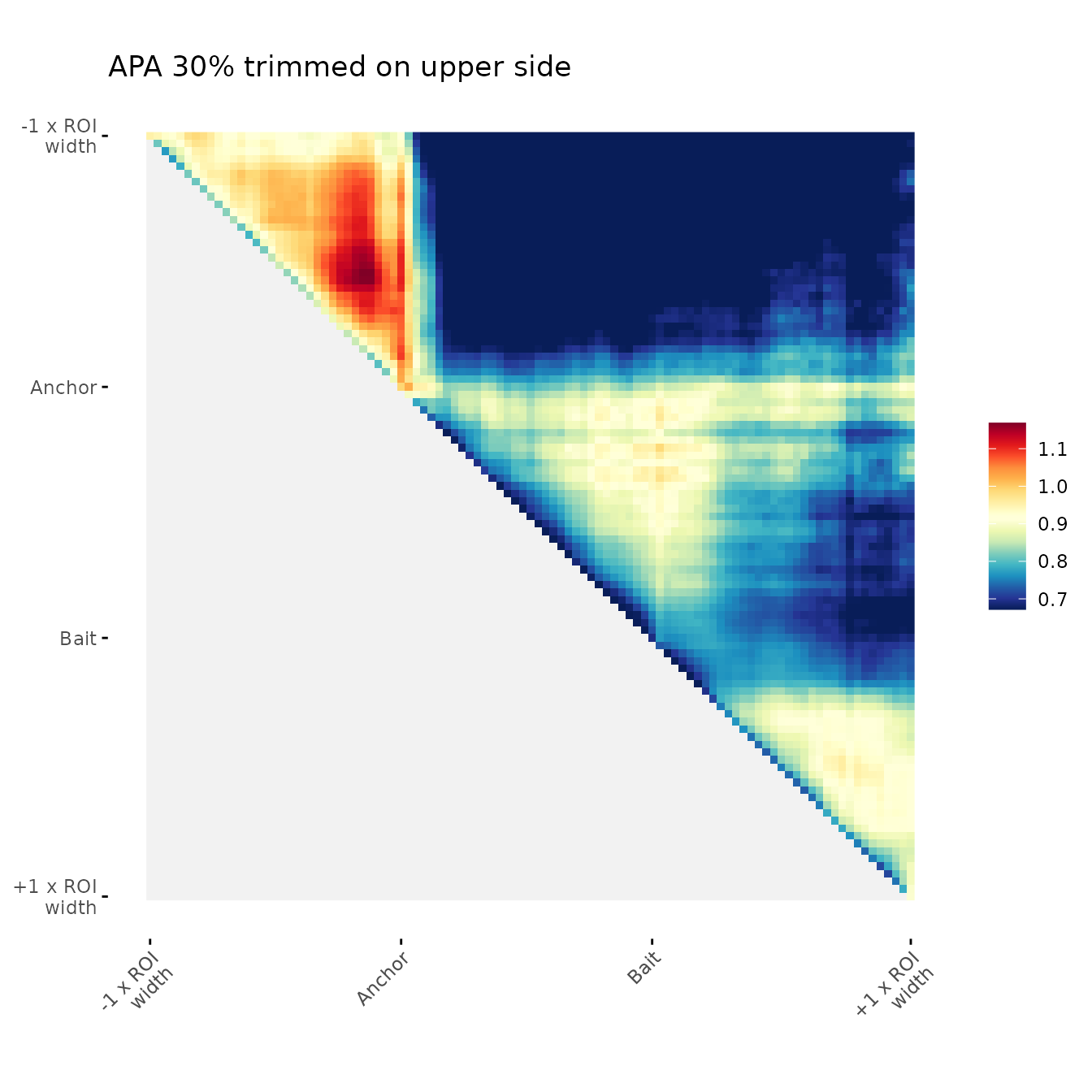
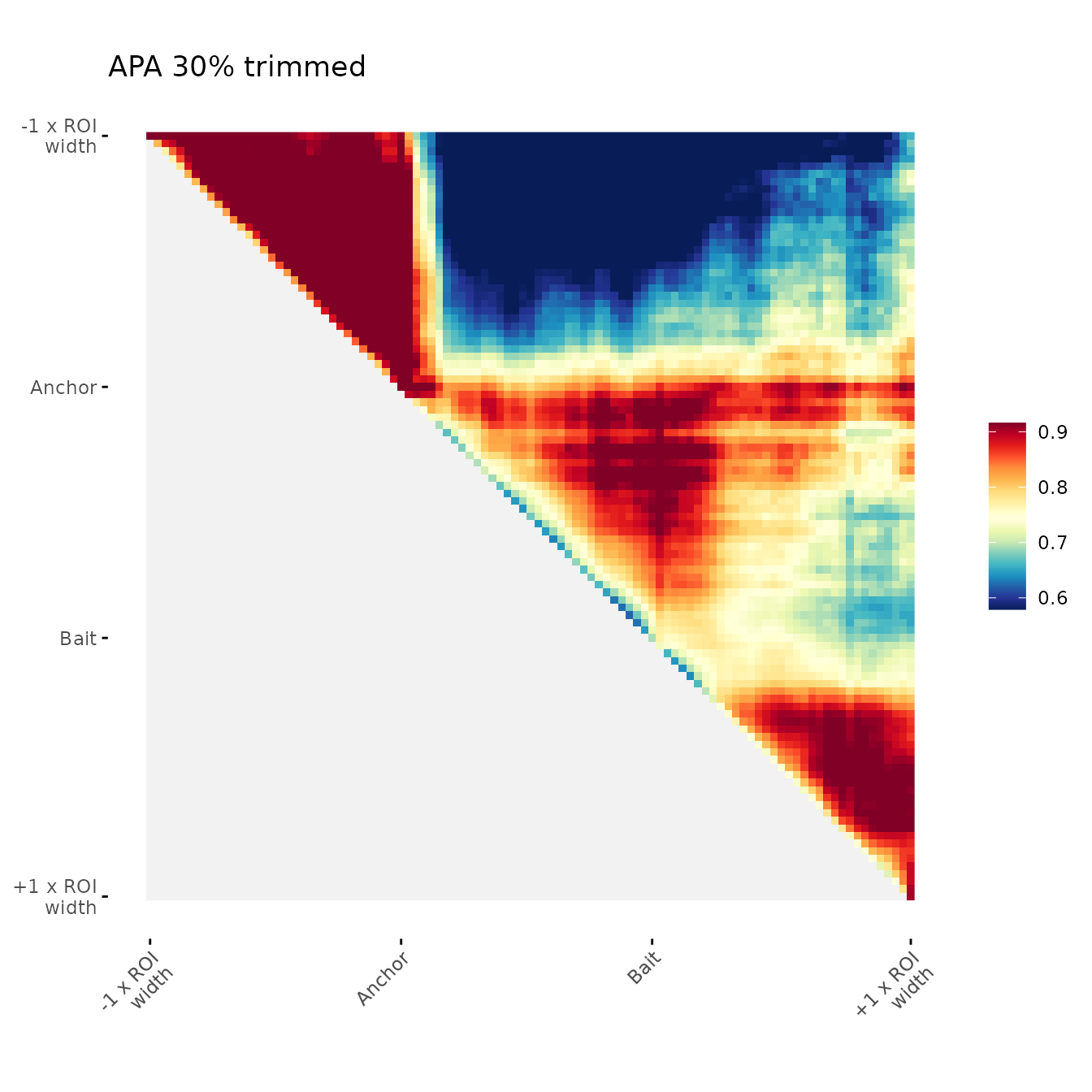
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA 30% trimmed",
trim = 30,
tails = "both"
)
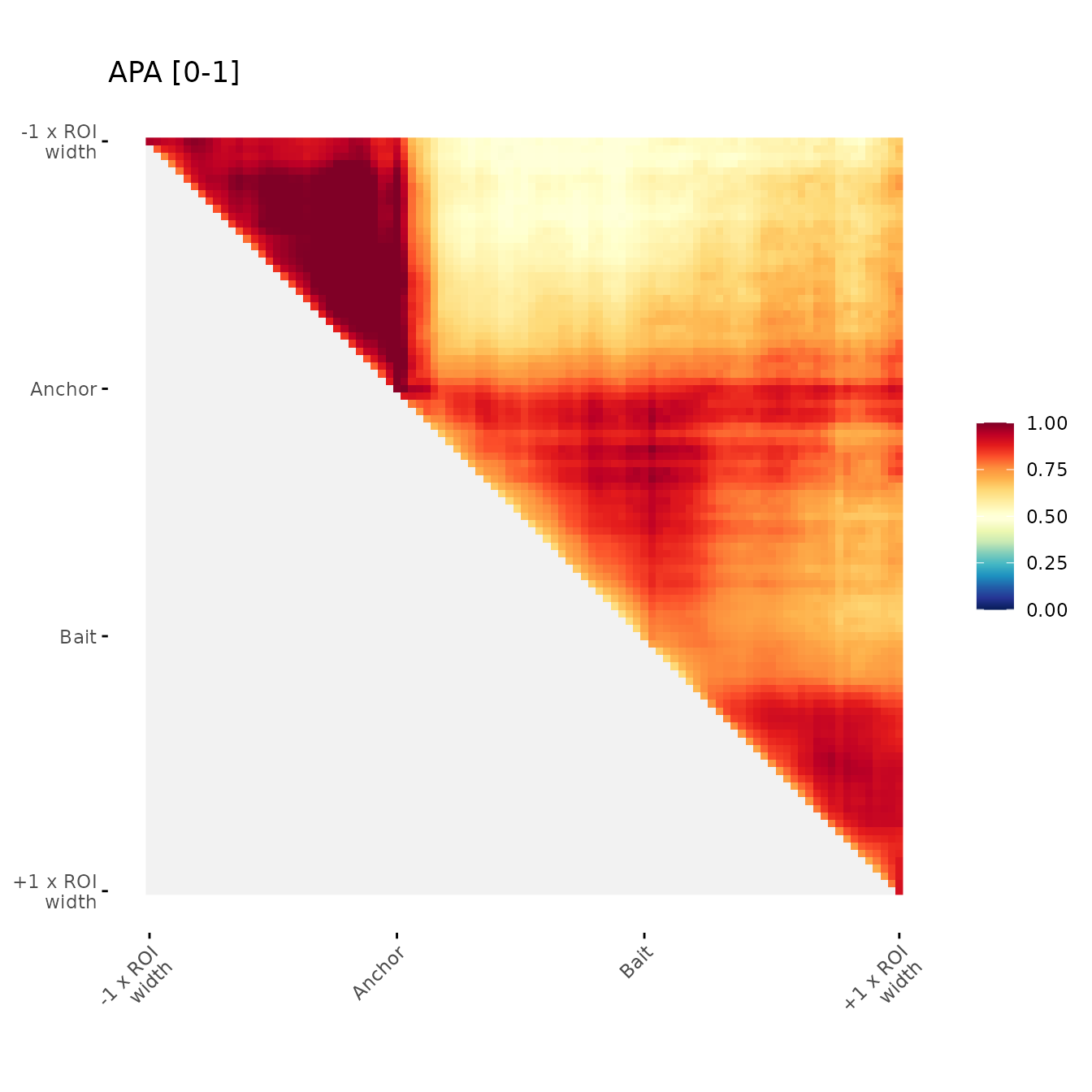
Modifying color scale:
Min and max color scale
Example of user-defined min and max color scale
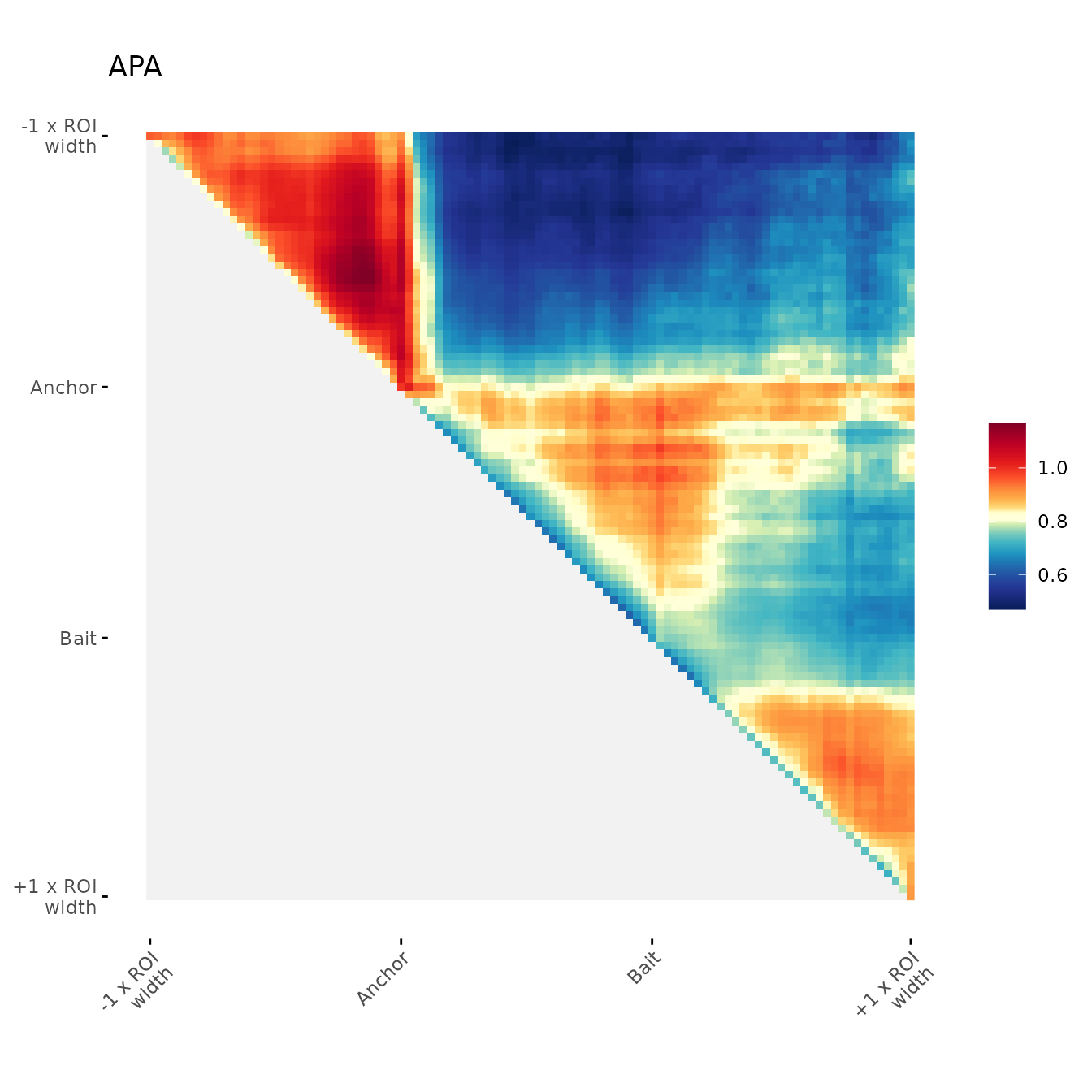
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA [0-1]",
colMin = 0,
colMax = 1
)
Center color scale
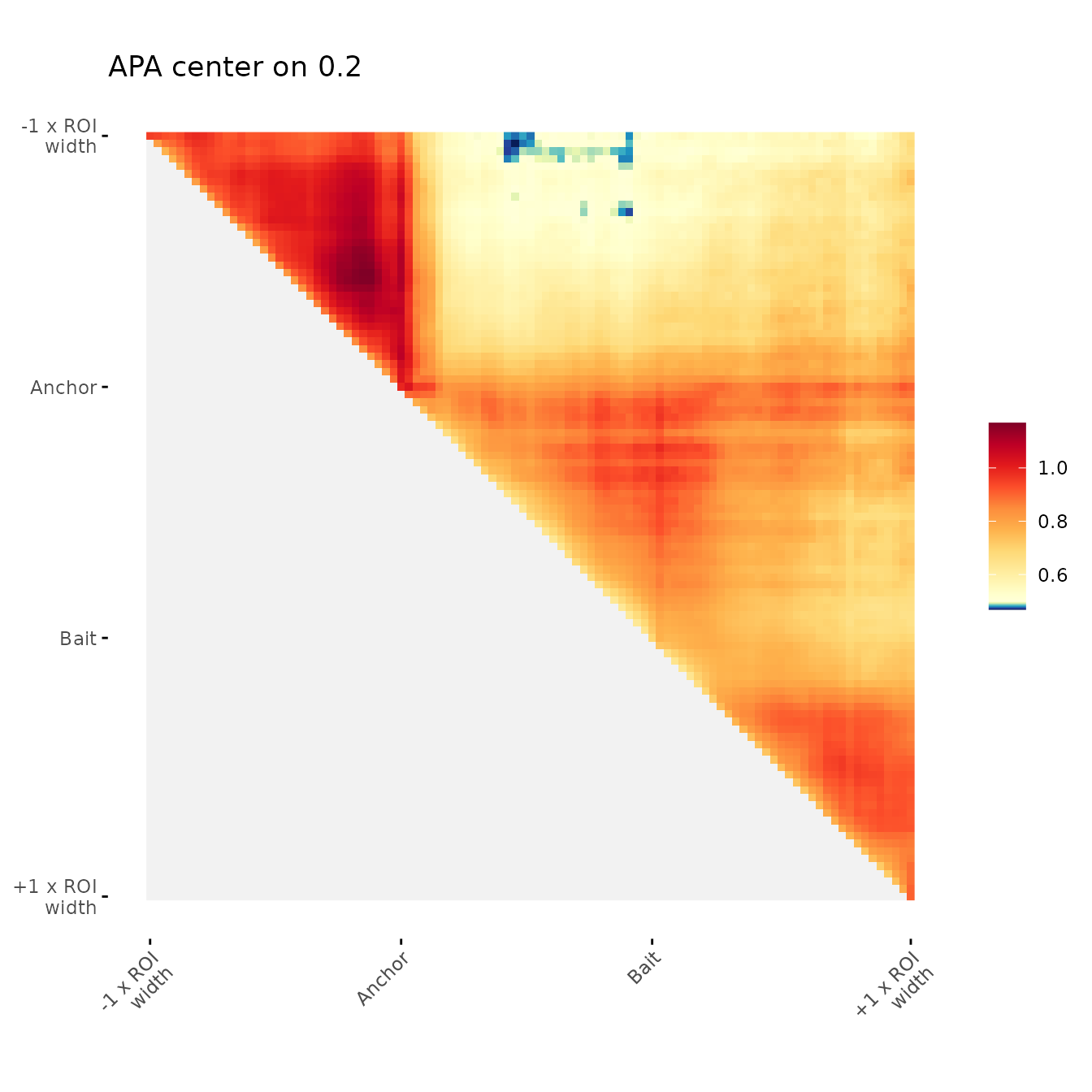
Example of user-defined color scale center
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA center on 0.2",
colMid = 0.5
)
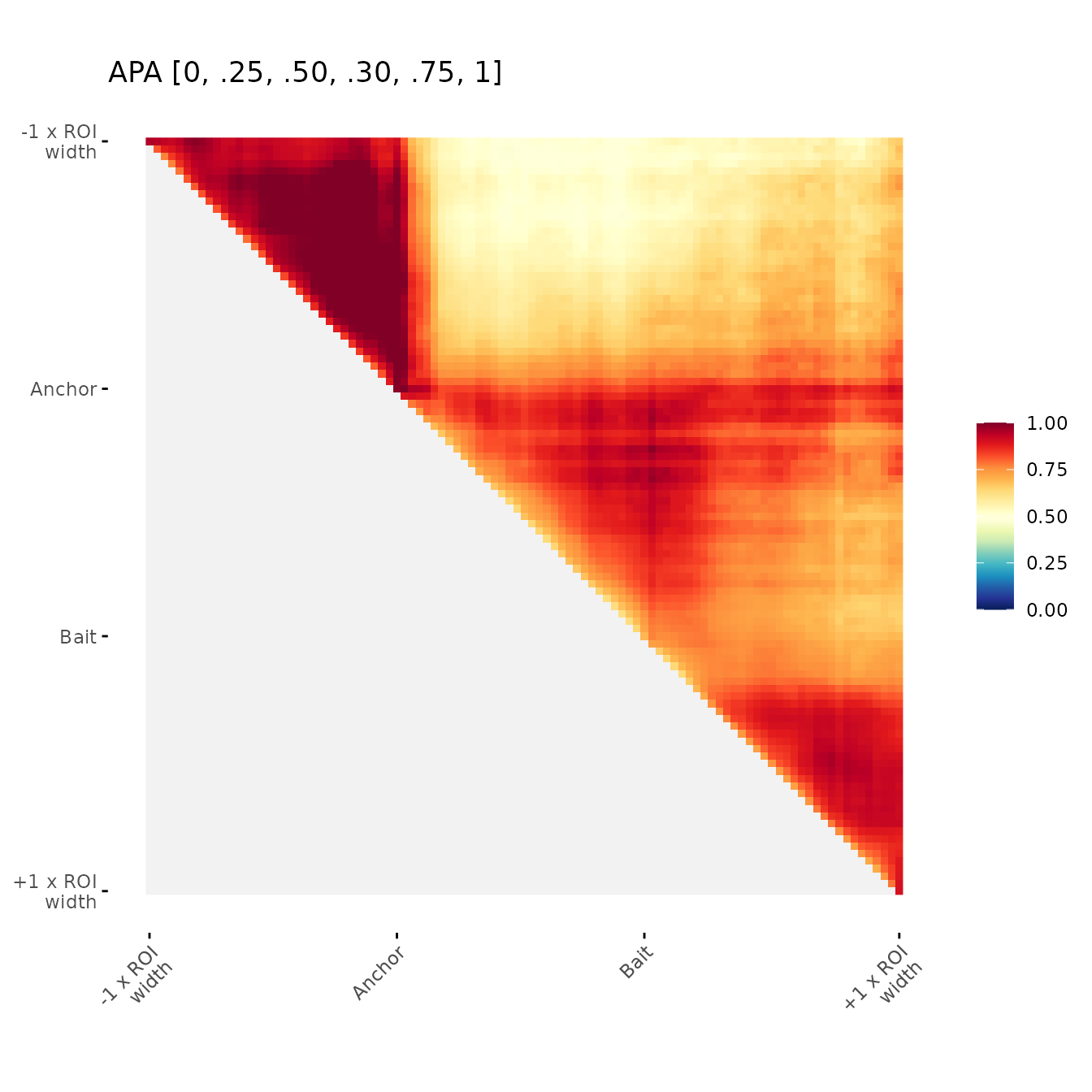
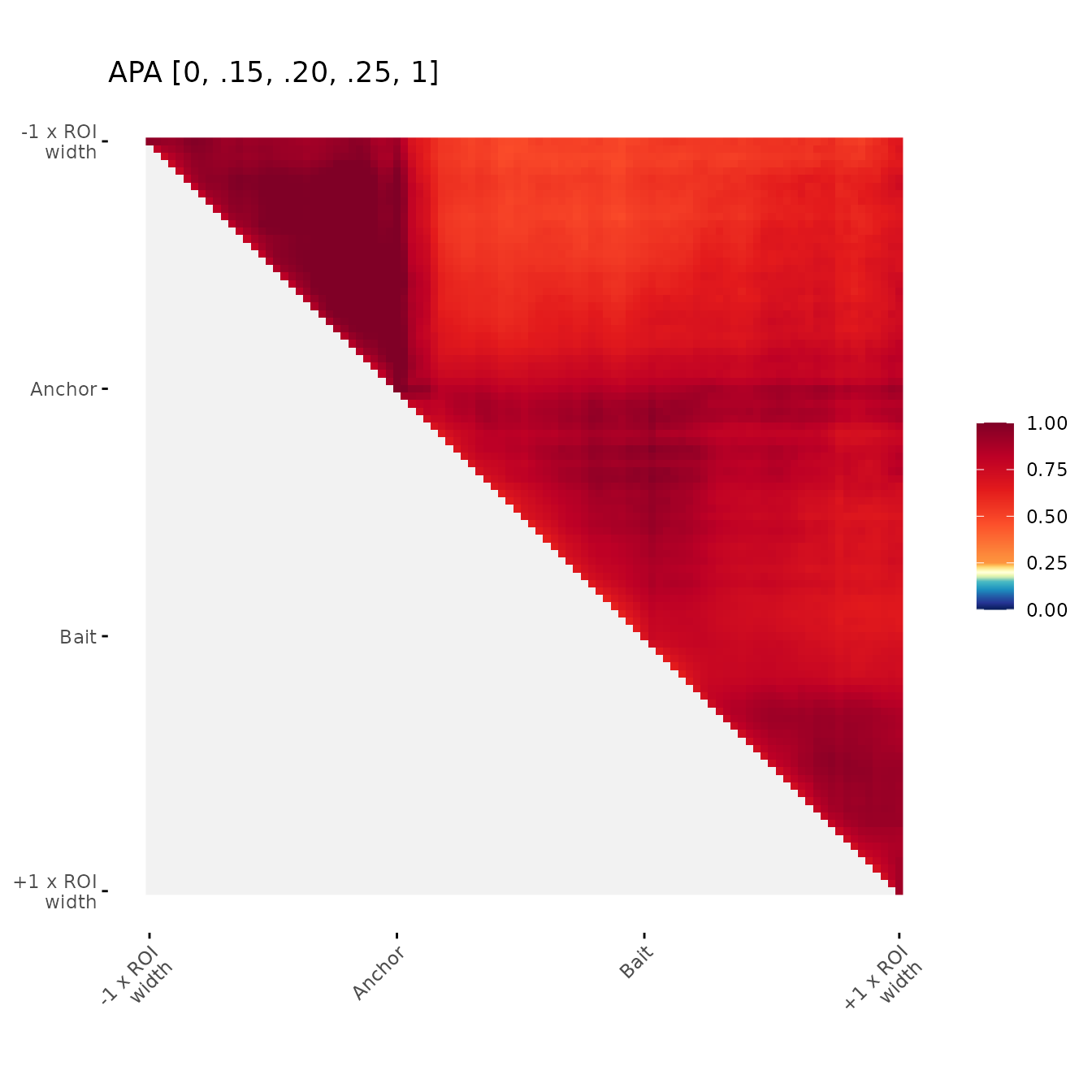
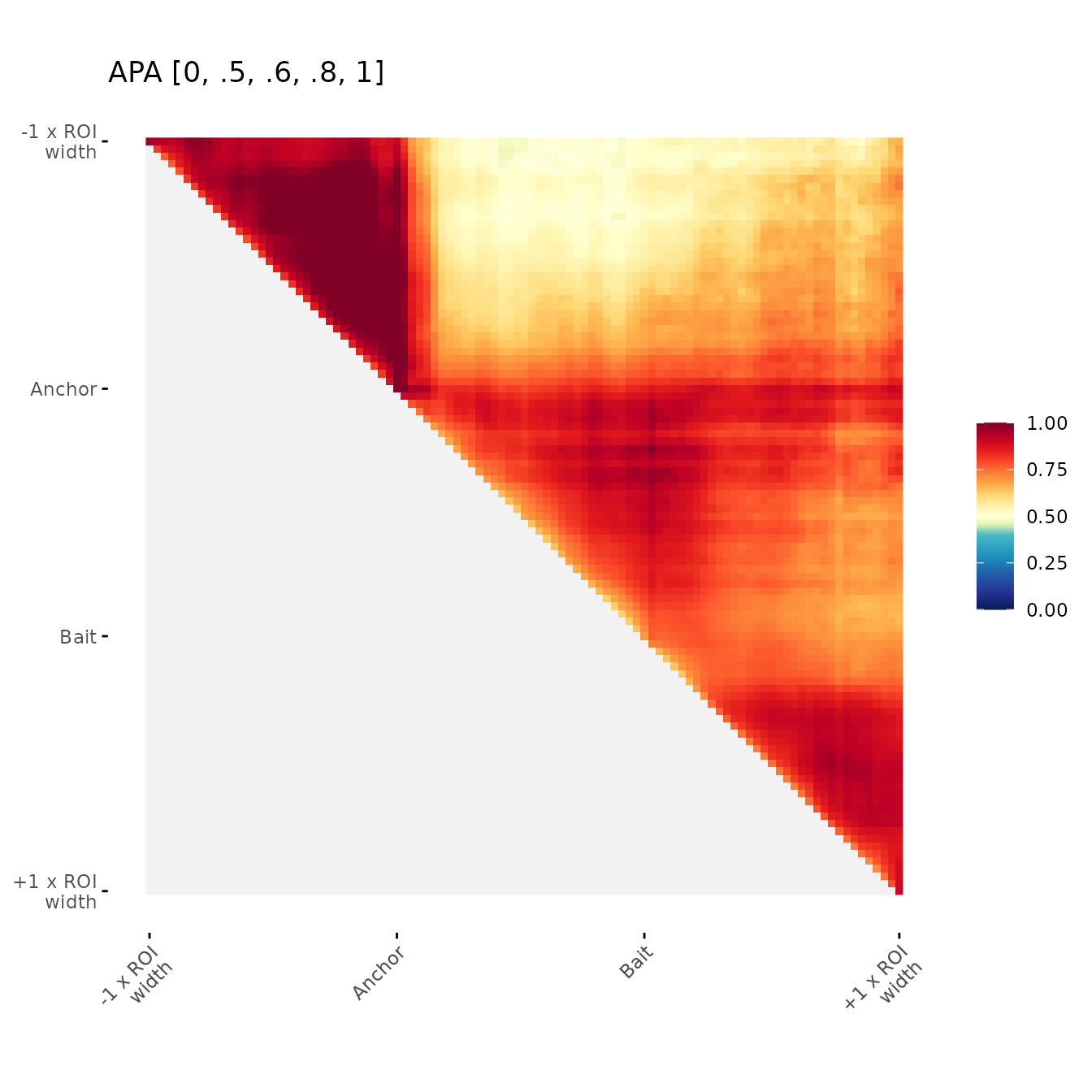
Change color breaks
Examples of user-defined color breaks
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA [0, .25, .50, .30, .75, 1]",
colBreaks = c(0,0.25,0.5,0.75,1)
)
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA [0, .15, .20, .25, 1]",
colBreaks = c(0,0.15,0.20,0.25,1)
)
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA [0, .5, .6, .8, 1]",
colBreaks = c(0,0.4,0.5,0.7,1)
)
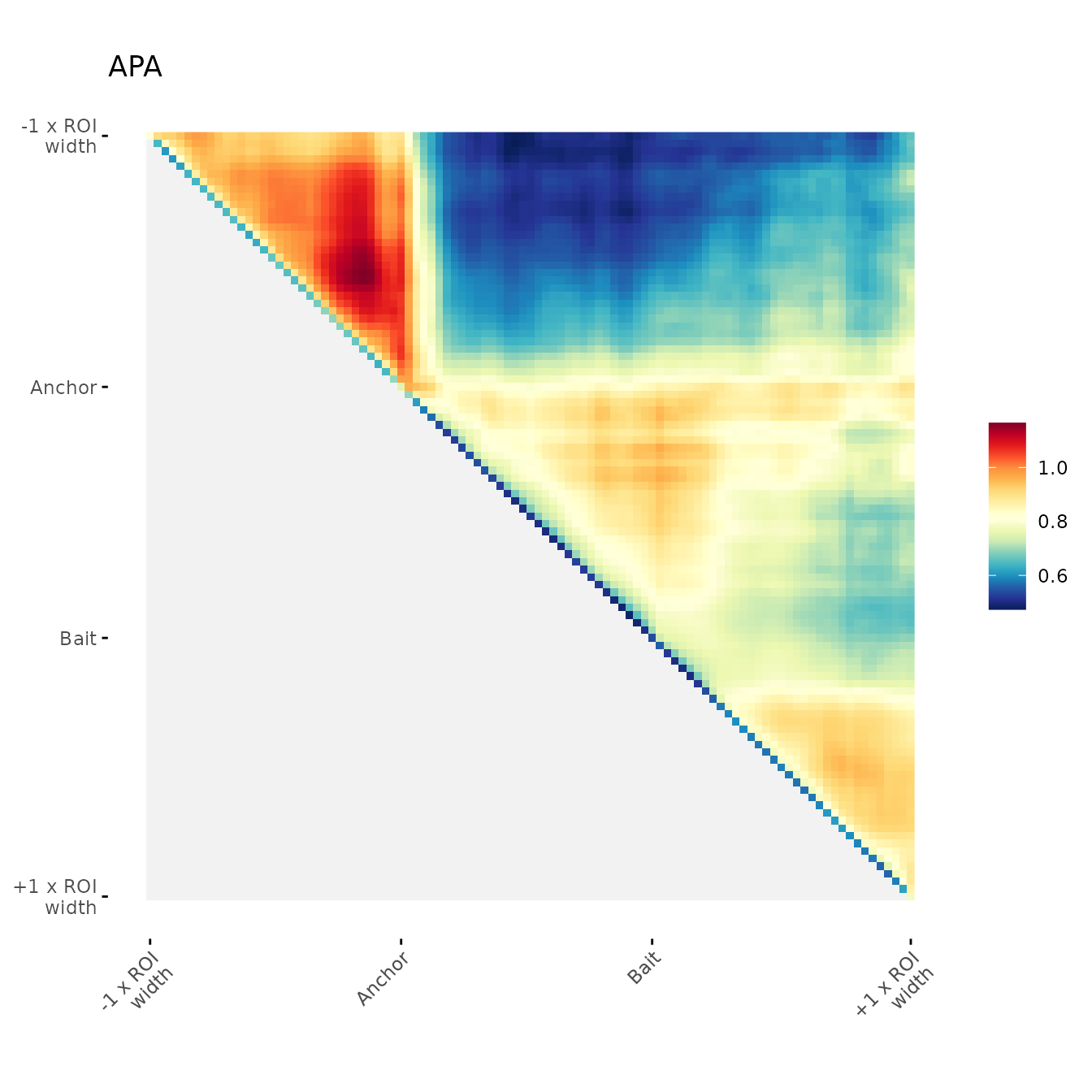
Blurred visualization
Option to apply a blurr on the heatmap to reduce noise.
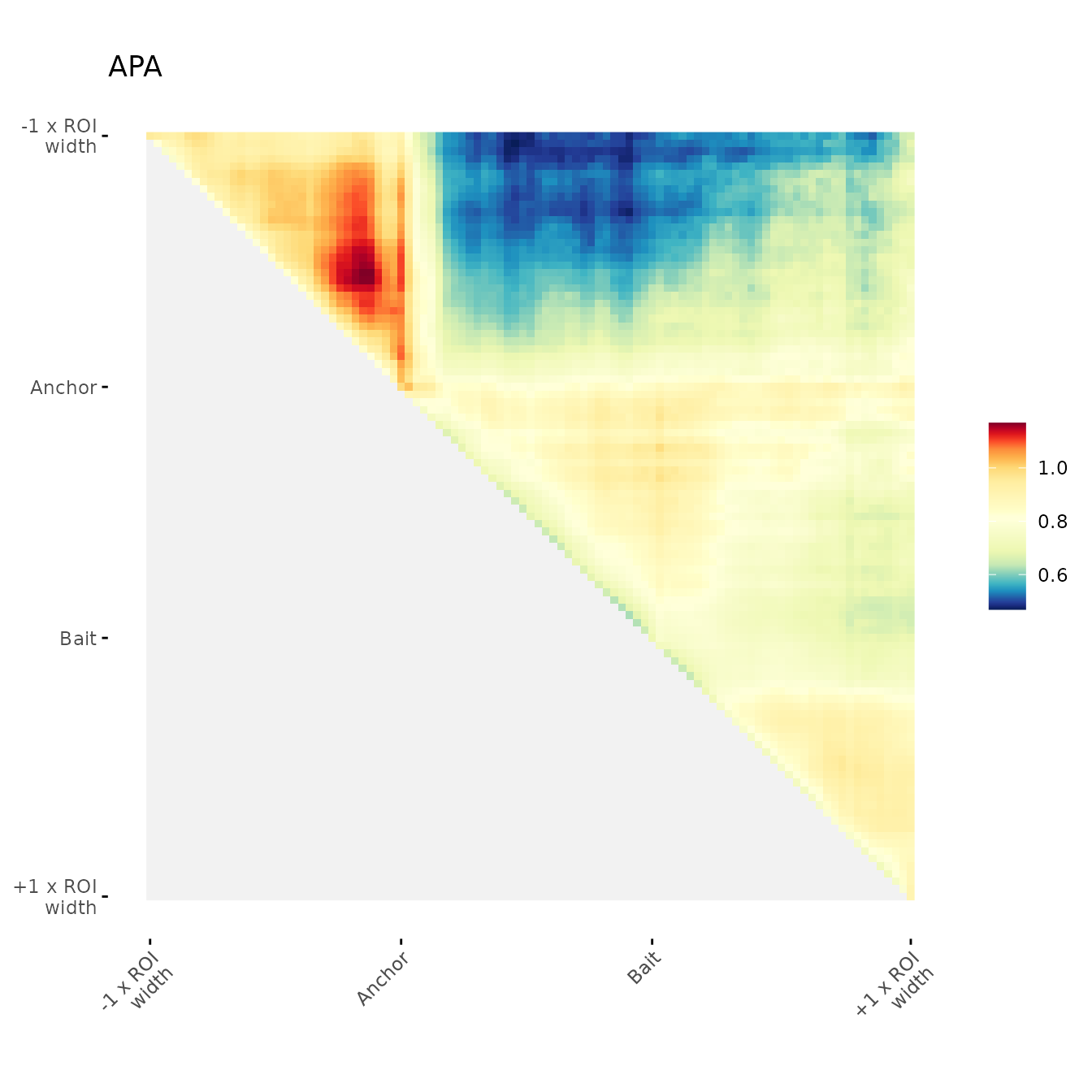
ggAPA(
aggregatedMtx = orientedAggreg.mtx,
title = "APA",
blurPass = 1,
stdev = 0.5,
loTri = NA
)
Session Info
sessionInfo()
#> R version 4.4.1 (2024-06-14)
#> Platform: x86_64-pc-linux-gnu
#> Running under: Ubuntu 22.04.4 LTS
#>
#> Matrix products: default
#> BLAS: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libblas.so.3
#> LAPACK: /usr/lib/x86_64-linux-gnu/openblas-pthread/libopenblasp-r0.3.20.so; LAPACK version 3.10.0
#>
#> locale:
#> [1] LC_CTYPE=C.UTF-8 LC_NUMERIC=C LC_TIME=C.UTF-8
#> [4] LC_COLLATE=C.UTF-8 LC_MONETARY=C.UTF-8 LC_MESSAGES=C.UTF-8
#> [7] LC_PAPER=C.UTF-8 LC_NAME=C LC_ADDRESS=C
#> [10] LC_TELEPHONE=C LC_MEASUREMENT=C.UTF-8 LC_IDENTIFICATION=C
#>
#> time zone: UTC
#> tzcode source: system (glibc)
#>
#> attached base packages:
#> [1] stats graphics grDevices utils datasets methods base
#>
#> other attached packages:
#> [1] HicAggR_1.1.3
#>
#> loaded via a namespace (and not attached):
#> [1] tidyselect_1.2.1 viridisLite_0.4.2
#> [3] farver_2.1.2 dplyr_1.1.4
#> [5] blob_1.2.4 filelock_1.0.3
#> [7] fastmap_1.2.0 reshape_0.8.9
#> [9] BiocFileCache_2.12.0 digest_0.6.36
#> [11] lifecycle_1.0.4 RSQLite_2.3.7
#> [13] magrittr_2.0.3 compiler_4.4.1
#> [15] rlang_1.1.4 sass_0.4.9
#> [17] tools_4.4.1 utf8_1.2.4
#> [19] yaml_2.3.9 data.table_1.15.4
#> [21] knitr_1.47 labeling_0.4.3
#> [23] S4Arrays_1.4.1 bit_4.0.5
#> [25] curl_5.2.1 DelayedArray_0.30.1
#> [27] xml2_1.3.6 plyr_1.8.9
#> [29] abind_1.4-5 BiocParallel_1.38.0
#> [31] withr_3.0.0 purrr_1.0.2
#> [33] BiocGenerics_0.50.0 desc_1.4.3
#> [35] grid_4.4.1 stats4_4.4.1
#> [37] fansi_1.0.6 colorspace_2.1-0
#> [39] Rhdf5lib_1.26.0 ggplot2_3.5.1
#> [41] scales_1.3.0 SummarizedExperiment_1.34.0
#> [43] cli_3.6.3 rmarkdown_2.27
#> [45] crayon_1.5.3 ragg_1.3.2
#> [47] generics_0.1.3 rstudioapi_0.16.0
#> [49] httr_1.4.7 DBI_1.2.3
#> [51] cachem_1.1.0 rhdf5_2.48.0
#> [53] stringr_1.5.1 zlibbioc_1.50.0
#> [55] parallel_4.4.1 XVector_0.44.0
#> [57] matrixStats_1.3.0 vctrs_0.6.5
#> [59] Matrix_1.7-0 jsonlite_1.8.8
#> [61] IRanges_2.38.1 S4Vectors_0.42.1
#> [63] bit64_4.0.5 systemfonts_1.1.0
#> [65] tidyr_1.3.1 strawr_0.0.91
#> [67] jquerylib_0.1.4 glue_1.7.0
#> [69] pkgdown_2.1.0 codetools_0.2-20
#> [71] stringi_1.8.4 gtable_0.3.5
#> [73] GenomeInfoDb_1.40.1 GenomicRanges_1.56.1
#> [75] UCSC.utils_1.0.0 munsell_0.5.1
#> [77] tibble_3.2.1 pillar_1.9.0
#> [79] htmltools_0.5.8.1 rhdf5filters_1.16.0
#> [81] GenomeInfoDbData_1.2.12 R6_2.5.1
#> [83] dbplyr_2.5.0 textshaping_0.4.0
#> [85] kableExtra_1.4.0 evaluate_0.24.0
#> [87] lattice_0.22-6 Biobase_2.64.0
#> [89] highr_0.11 backports_1.5.0
#> [91] memoise_2.0.1 bslib_0.7.0
#> [93] Rcpp_1.0.12 InteractionSet_1.32.0
#> [95] svglite_2.1.3 gridExtra_2.3
#> [97] SparseArray_1.4.8 checkmate_2.3.1
#> [99] xfun_0.45 fs_1.6.4
#> [101] MatrixGenerics_1.16.0 pkgconfig_2.0.3